ChromosomePage
15
15
Clinical Syndrome: Klinefelter
Estimated Frequency Birth: 1/500 male borth
Main Phenotypic Characteristics:
Pitched voice, Male, subfertile with small testes, developed breasts, feminine, long limbs.
Slide 95
Found in certain tissues e.g., salivary glands of larvae, gut epithelium, Malphigian tubules and some fat bodies, of some Diptera (Drosophila, Sciara, Rhyncosciara)
These chromosomes are very long and thick (upto 200 times their size during mitotic metaphase in the case of Drosophila)
Hence they are known as Giant chromosomes.
Giant chromosomes
Slide 96
They are first discovered by Balbiani in 1881 in dipteran salivary glands and thus also known as salivary gland chromosomes.
But their significance was realized only after the extensive studies by Painter during 1930’s.
Giant chromosomes have also been discovered in suspensors of young embryos of many plants, but these do not show the bands so typical of salivary gland chromosomes.
Slide 97
He described the morphology in detail and discovered the relation between salivary gland chromosomes and germ cell chromosomes.
Slides of Drosophila giant chromosomes are prepared by squashing in acetocarmine the salivary glands dissected out from the larvae.
The total length of D.melanogater giant chromosomes is about 2,000µ.
Slide 98
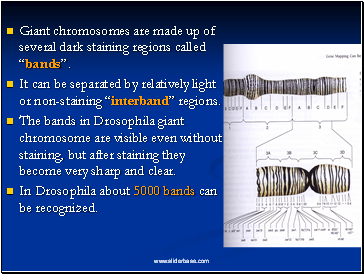
Giant chromosomes are made up of several dark staining regions called “bands”.
It can be separated by relatively light or non-staining “interband” regions.
The bands in Drosophila giant chromosome are visible even without staining, but after staining they become very sharp and clear.
In Drosophila about 5000 bands can be recognized.
Slide 99
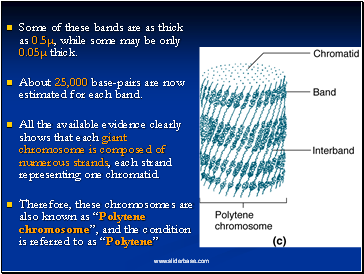
Some of these bands are as thick as 0.5µ, while some may be only 0.05µ thick.
About 25,000 base-pairs are now estimated for each band.
All the available evidence clearly shows that each giant chromosome is composed of numerous strands, each strand representing one chromatid.
Therefore, these chromosomes are also known as “Polytene chromosome”, and the condition is referred to as “Polytene”
Slide 100
The numerous strands of these chromosomes are produced due to repeated replication of the paired chromosomes without any nuclear or cell division.
So that the number of strands (chromatids) in a chromosome doubles after every round of DNA replication
It is estimated that giant chromosomes of Drosophila have about 1,024 strands
Contents
- What Exactly is a chromosome?
- Number of chromosomes
- Chromosome Size
- Euchromatin and Heterochromatin
- Satellite DNAs
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosomes
- Prokaryotic chromosome
- Bacterial Chromosome
- Supercoiling
- Mechanism of folding of a bacterial chromosome
- Chromatin
- Centromeres and Telomeres
- Centromere
- Kinetochore
- Telomere
- Telomere Repeat Sequences
- Staining and Banding chromosome
- Chromosomal Aberrations
- Structural Chromosomal Aberrations
- Deletion or deficiency
- Deletion in Prokaryotes
- Duplication
- Origin
- Inversion
- Inversions in natural populations
- Translocation
- Non-Disjunction
- Variation in chromosome number
- More about Aneuploidy
- Uses of Aneuploidy
- Trisomy in Humans
- Amniocentesis for Detecting Aneuploidy
- Other Syndromes
- Giant chromosomes
- Lampbrush Chromosome
- Dosage Compensation
- Barr Bodies
- Mechanism of X-chromosome Inactivation
- Reading assignment
Last added presentations
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Motion
- Madame Marie Curie