ChromosomePage
10
10
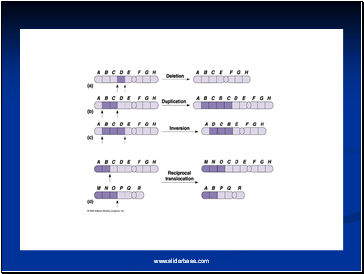
Consider a normal chromosome with genes in alphabetical order: a b c d e f g h i
1. Deletion: part of the chromosome has been removed: a b c g h i
2. Dupliction: part of the chromosome is duplicated:
a b c d e f d e f g h i
3. Inversion: part of the chromosome has been re-inserted in reverse order: a b c f e d g h i
ring: the ends of the chromosome are joined together to make a ring
Slide 64
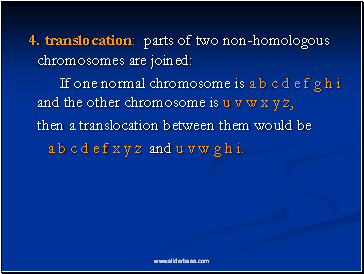
4. translocation: parts of two non-homologous chromosomes are joined:
If one normal chromosome is a b c d e f g h i and the other chromosome is u v w x y z,
then a translocation between them would be
a b c d e f x y z and u v w g h i.
Slide 65
Slide 66
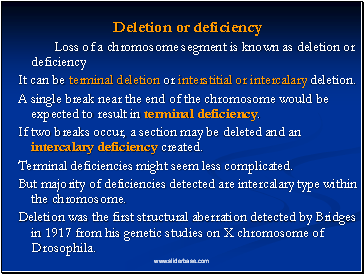
Deletion or deficiency
Loss of a chromosome segment is known as deletion or deficiency
It can be terminal deletion or interstitial or intercalary deletion.
A single break near the end of the chromosome would be expected to result in terminal deficiency.
If two breaks occur, a section may be deleted and an intercalary deficiency created.
Terminal deficiencies might seem less complicated.
But majority of deficiencies detected are intercalary type within the chromosome.
Deletion was the first structural aberration detected by Bridges in 1917 from his genetic studies on X chromosome of Drosophila.
Slide 67
Deletion generally produce striking genetic and physiological effects.
When homozygous, most deletions are lethal, because most genes are necessary for life and a homozygous deletion would have zero copies of some genes.
When heterozygous, the genes on the normal homologue are hemizygous: there is only 1 copy of those genes.
Crossing over is absent in deleted region of a chromosome since this region is present in only one copy in deletion heterozygotes.
In Drosophila, several deficiencies induced the mutants like Blond, Pale, Beaded, Carved, Notch, Minute etc.
Slide 68
Deletion in Prokaryotes
Deletions are found in prokaryotes as well, e.g., E.coli, T4 phage and Lambda phage.
In E.coli, deletions of up to 1 % of the bacterial chromosome are known.
In lambda phage, however 20% of the genome may be missing in some of the deletions.
Deletion in Human:
Chromosome deletions are usually lethal even as heterozygotes, resulting in zygotic loss, stillbirths, or infant death.
Sometimes, infants with small chromosome deficiencies however, survive long enough to permit the abnormal phenotype they express.
Slide 69
Contents
- What Exactly is a chromosome?
- Number of chromosomes
- Chromosome Size
- Euchromatin and Heterochromatin
- Satellite DNAs
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosomes
- Prokaryotic chromosome
- Bacterial Chromosome
- Supercoiling
- Mechanism of folding of a bacterial chromosome
- Chromatin
- Centromeres and Telomeres
- Centromere
- Kinetochore
- Telomere
- Telomere Repeat Sequences
- Staining and Banding chromosome
- Chromosomal Aberrations
- Structural Chromosomal Aberrations
- Deletion or deficiency
- Deletion in Prokaryotes
- Duplication
- Origin
- Inversion
- Inversions in natural populations
- Translocation
- Non-Disjunction
- Variation in chromosome number
- More about Aneuploidy
- Uses of Aneuploidy
- Trisomy in Humans
- Amniocentesis for Detecting Aneuploidy
- Other Syndromes
- Giant chromosomes
- Lampbrush Chromosome
- Dosage Compensation
- Barr Bodies
- Mechanism of X-chromosome Inactivation
- Reading assignment
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Health Physics
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions