ChromosomePage
16
16
In the case of Chironomous may have about 4,096 strands.
The bands of giant chromosomes are formed as a result of stacking over one another of the chromomeres of all strands present in them.
Slide 101
Since chromatin fibers are highly coiled in chromosomes, they stain deeply.
On the other hand, the chromatin fibers in the interband regions are fully extended, as a result these regions take up very light stain.
In Drosophila the location of many genes is correlated with specific bands in the connected chromosomes.
In interband region do not have atleast functional genes
Slide 102
During certain stages of development, specific bands and inter band regions are associated with them greatly increase in diameter and produced a structure called Puffs or Balbiani rings.
Puffs are believed to be produced due to uncoiling of chromatin fibers present in the concerned chromomeres.
The puffs are sites of active RNA synthesis.
Slide 103
Slide 104
Figure 3. Polytene chromosome map of Anopheles gambiae
Slide 105
Lampbrush Chromosome
It was given this name because it is similar in appearance to the brushes used to clean lamp chimneys in centuries past.
First observed by Flemming in 1882.
The name lampbrush was given by Ruckert in 1892.
These are found in oocytic nuclei of vertebrates (sharks, amphibians, reptiles and birds)as well as in invertebrates (Sagitta, sepia, Ehinaster and several species of insects).
Also found in plants – but most experiments in oocytes.
Slide 106
Lampbrush chromosomes are up to 800 µm long; thus they provide very favorable material for cytological studies.
The homologous chromosomes are paired and each has duplicated to produce two chromatids at the lampbrush stage.
Each lampbrush chromosome contains a central axial region, where the two chromatids are highly condensed
Each chromosome has several chromomeres distributed over its length.
From each chromomere, a pair of loops emerges in the opposite directions vertical to the main chromosomal axis.
Slide 107
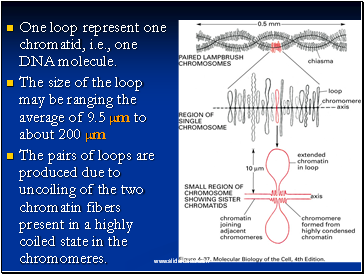
One loop represent one chromatid, i.e., one DNA molecule.
The size of the loop may be ranging the average of 9.5 µm to about 200 µm
The pairs of loops are produced due to uncoiling of the two chromatin fibers present in a highly coiled state in the chromomeres.
Contents
- What Exactly is a chromosome?
- Number of chromosomes
- Chromosome Size
- Euchromatin and Heterochromatin
- Satellite DNAs
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosomes
- Prokaryotic chromosome
- Bacterial Chromosome
- Supercoiling
- Mechanism of folding of a bacterial chromosome
- Chromatin
- Centromeres and Telomeres
- Centromere
- Kinetochore
- Telomere
- Telomere Repeat Sequences
- Staining and Banding chromosome
- Chromosomal Aberrations
- Structural Chromosomal Aberrations
- Deletion or deficiency
- Deletion in Prokaryotes
- Duplication
- Origin
- Inversion
- Inversions in natural populations
- Translocation
- Non-Disjunction
- Variation in chromosome number
- More about Aneuploidy
- Uses of Aneuploidy
- Trisomy in Humans
- Amniocentesis for Detecting Aneuploidy
- Other Syndromes
- Giant chromosomes
- Lampbrush Chromosome
- Dosage Compensation
- Barr Bodies
- Mechanism of X-chromosome Inactivation
- Reading assignment
Last added presentations
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Motion
- Waves & Sound
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Upcoming Classes
- Mechanics Lecture