FrictionPage
1
1
Slide 1
Types of Friction
Force of Kinetic Friction
This value represents the relative force necessary to keep an object moving at a constant rate
Force of Static Friction
This value represents the relative force necessary to make an object move
Slide 2
Frictional Force Resisting Motion
Force Causing the Object to Move
Kinetic Region
Static Region
Max
Slide 3
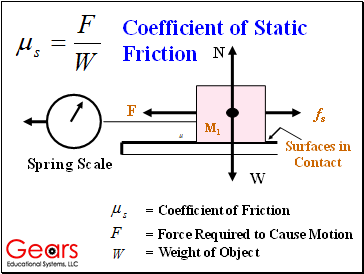
Frictional Forces Occur When Materials are in Contact
W
fs
F
N
Surfaces in Contact
M1
Spring Scale
F = Force Causing Motion (Pull on Scale)
Fs = Force of Static Friction (Resists Motion)
N = Force Normal Holds Surfaces in Contact
W = Weight of Object ( Mass x Gravity)
Slide 4
Friction is a Force That Resists Motion
W
fs
F
N
Surfaces in Contact
The Pink Block M1 Will not Move Until the Force F (Pull on the scale ) Exceeds the Force of Static Friction fs.
M1
Spring Scale
Slide 5
The Relative Force of Static Friction Between 2 Objects is Expressed as the Quotient of the Force (F) Required to Move the Object
W
fs
F
N
Surfaces in Contact
M1
Spring Scale
Divided by the Weight W of the Object
This is Called the Coefficient of Friction
Slide 6
W
fs
F
N
Surfaces in Contact
M1
Spring Scale
= Force Required to Cause Motion
= Weight of Object
= Coefficient of Friction
Coefficient of Static Friction
Slide 7
Using the Gears-IDS Battery to Calculate The Static
Coefficient of Friction
Slide 8
Record the Maximum Force (F) (Before the Battery Begins to Move)
Maximum Force F = 110 g
Slide 9
Record the Weight (W ) of the Battery
580 g
Slide 10
The Coefficient of Static Friction Between the Wood Desktop and the Plastic Battery is Described Algebraically:
= 580 g
= 110 g
= .190
Slide 11
The Coefficient of Kinetic Friction Can be Found Using the Same Technique
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Madame Marie Curie
- Solar Energy
- Gravitation
- Sound
- Upcoming Classes
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal