Health PhysicsPage
1
1
Slide 1
By the end of this lesson, and for the exam, you should be able to:
Describe one medical use of radiation based on the fact that that it can destroy cells (instrument sterilisation, treatment of cancer) (General level).
Describe one medical use of radiation based on the fact that radiation is easy to detect (General level).
Slide 2
There are 3 main uses of ionising radiation in medicine:
Treatment
Diagnosis
Sterilisation
Slide 3
What is Cancer?
Cancers are growths of cells (cancerous tumours) which are out of control. As a result of this, they do not perform their intended function.
Slide 4
Treatment of Cancer
Cancerous tumours can be treated using the following main methods:
Chemotherapy (drugs).
Radiation therapy (radiotherapy and brachytherapy).
Surgery.
Slide 5
Factors Which Affect the Choice of Treatment for Cancer
The size of the tumour.
The position of the tumour.
The choice of treatment depends on a number of factors including:
Slide 6
The Aims of Radiation Therapy
The aim of radiation therapy is to cause damage to the cancerous cells whilst minimising the risk to surrounding healthy tissue.
The damage inflicted by radiation therapy causes the cancerous cells to stop reproducing and thus the tumour shrinks.
Unfortunately, healthy cells can also be damaged by the radiation.
Slide 7
Why does the amount of radiation given to the patient have to be accurately calculated?
The amount of radiation given to the patient has to be accurately calculated so that the damage is limited to the cancerous cells only.
Slide 8
Radiation Therapy
Radiotherapy
Brachytherapy
Radiation therapy uses ionising radiation to treat cancer i.e. to destroy cancerous cells.
There are two techniques in radiation therapy that are used to treat cancer using ionising radiation:
Slide 9
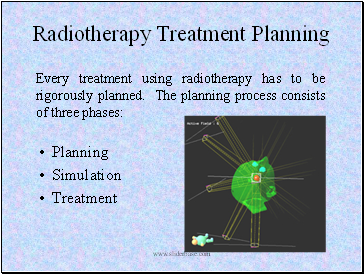
Radiotherapy Treatment Planning
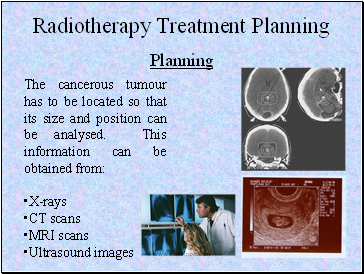
Planning
Simulation
Treatment
Every treatment using radiotherapy has to be rigorously planned. The planning process consists of three phases:
Slide 10
Contents
- What is Cancer?
- Treatment of Cancer
- The Aims of Radiation Therapy
- Radiation Therapy
- Radiotherapy Treatment Planning
- Radiotherapy Treatment
- Treatment of Cancer
- Tracers
- Nuclear Medicine Tracers
- The Gamma Camera
- Diagnosis Static Imaging
- Performing the Renogram
- Diagnosis The Renogram
- Sterilisation
Last added presentations
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Health Physics
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Newton's laws of motion
- Newton’s laws of motion