ChromosomePage
17
17
Slide 108
One end of each loop is thinner (thin end) than the other end (thick end).
There is extensive RNA synthesis at the thin end of the loops, while there is little or no RNA synthesis at the thick end.
Slide 109
Phase-contrast and fluorescent micrographs of
lampbrush chromosomes
Slide 110
Dosage Compensation
Sex Chromosomes: females XX, males XY
Females have two copies of every X-linked gene; males have only one.
How is this difference in gene dosage compensated for? OR
How to create equal amount of X chromosome gene products in males and females?
Slide 111
Levels of enzymes or proteins encoded by genes on the X chromosome are the same in both males and females
Even though males have 1 X chromosome and females have 2.
Slide 112
G6PD, glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase, gene is carried on the X chromosome
This gene codes for an enzyme that breaks down sugar
Females produce the same amount of G6PD enzyme as males
XXY and XXX individuals produce the same about of G6PD as anyone else
Slide 113
In cells with more than two X chromosomes, only one X remains genetically active and all the others become inactivated.
In some cells the paternal allele is expressed
In other cells the maternal allele is expressed
In XXX and XXXX females and XXY males only 1 X is activated in any given cell the rest are inactivated
Slide 114
Slide 115
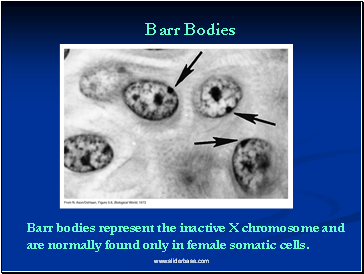
Barr Bodies
1940’s two Canadian scientists noticed a dark staining mass in the nuclei of cat brain cells
Found these dark staining spots in female but not males
This held for cats and humans
They thought the spot was a tightly condensed X chromosome
Slide 116
Barr bodies represent the inactive X chromosome and are normally found only in female somatic cells.
Barr Bodies
Slide 117
A woman with the chromosome constitution 47, XXX should have 2 Barr bodies in each cell.
XXY individuals are male, but have a Barr body.
XO individuals are female but have no Barr bodies.
Slide 118
Contents
- What Exactly is a chromosome?
- Number of chromosomes
- Chromosome Size
- Euchromatin and Heterochromatin
- Satellite DNAs
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosomes
- Prokaryotic chromosome
- Bacterial Chromosome
- Supercoiling
- Mechanism of folding of a bacterial chromosome
- Chromatin
- Centromeres and Telomeres
- Centromere
- Kinetochore
- Telomere
- Telomere Repeat Sequences
- Staining and Banding chromosome
- Chromosomal Aberrations
- Structural Chromosomal Aberrations
- Deletion or deficiency
- Deletion in Prokaryotes
- Duplication
- Origin
- Inversion
- Inversions in natural populations
- Translocation
- Non-Disjunction
- Variation in chromosome number
- More about Aneuploidy
- Uses of Aneuploidy
- Trisomy in Humans
- Amniocentesis for Detecting Aneuploidy
- Other Syndromes
- Giant chromosomes
- Lampbrush Chromosome
- Dosage Compensation
- Barr Bodies
- Mechanism of X-chromosome Inactivation
- Reading assignment
Last added presentations
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Gravitation
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions