Newton’s laws of motionPage
1
1
Slide 1
This lecture will help you understand:
Newton’s First Law of Motion
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
Forces and Interactions
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Summary of Newton’s Three Laws
Slide 2
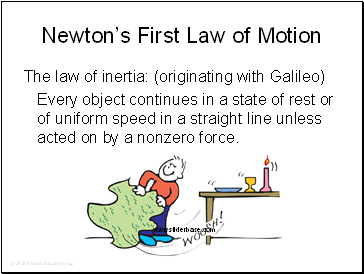
Newton’s First Law of Motion
The law of inertia: (originating with Galileo)
Every object continues in a state of rest or of uniform speed in a straight line unless acted on by a nonzero force.
Slide 3
A sheet of paper can be quickly withdrawn from under a soft-drink can without the can toppling, because
A. gravity pulls harder on the can than on the paper.
the can has weight.
the can has inertia.
None of the above.
Newton’s First Law of Motion
CHECK YOUR NEIGHBOR
Slide 4
A sheet of paper can be quickly withdrawn from under a soft-drink can without the can toppling, because
A. gravity pulls harder on the can than on the paper.
the can has weight.
the can has inertia.
None of the above.
Newton’s First Law of Motion
CHECK YOUR ANSWER
Slide 5
If you swing a stone overhead in a horizontal circle and the string breaks, the tendency of the stone is to follow a
A. curved path.
straight-line path.
spiral path.
vertical path.
Newton’s First Law of Motion
CHECK YOUR NEIGHBOR
Slide 6
If you swing a stone overhead in a horizontal circle and the string breaks, the tendency of the stone is to follow a
A. curved path.
straight-line path.
spiral path.
vertical path.
Newton’s First Law of Motion
CHECK YOUR ANSWER
Slide 7
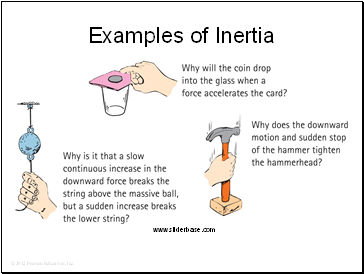
Examples of Inertia
Slide 8
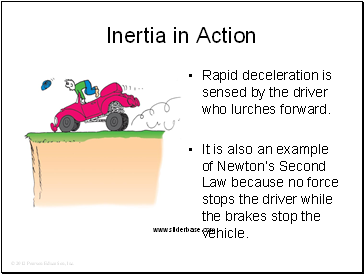
Inertia in Action
Rapid deceleration is sensed by the driver who lurches forward.
It is also an example of Newton’s Second Law because no force stops the driver while the brakes stop the vehicle.
Slide 9
Inertia in Action
When you flip a coin in a high-speed airplane, it behaves as if the airplane were at rest.
The coin keeps up with you.
Slide 10
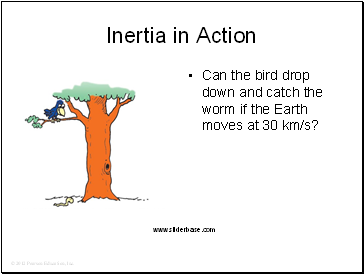
Inertia in Action
Can the bird drop down and catch the worm if the Earth moves at 30 km/s?
Contents
- Newton’s First Law of Motion
- Inertia in Action
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion
- Forces and Interactions
- Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Last added presentations
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Thermal Energy
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy