Direct heat utilization of geothermal energyPage
1
1
Slide 1
Slide 2
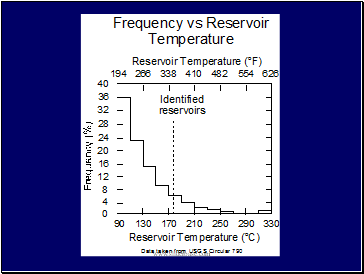
World Wide Direct Utilization
Approximately 72 countries
Installed capacity: 28,268 MWt
Energy Use: 273,372 TJ/yr (75,943 GWh/yr) (enough to heat 3.4 million homes)
Saving 129 million bbl (19.2 mill. tonnes) of oil per year
Largest use: geothermal (ground-source) heat pumps used for both heating and cooling
World Wide
Slide 3
What is Direct-Use: Heating and Cooling
Swimming, bathing and balneology
Space heating and cooling
Including district energy (heating/cooling) systems
Agriculture applications
Greenhouse heating
Aquaculture applications
Fish pond and raceway heating
Industrial processes
Including food and grain drying
Geothermal heat pumps
Slide 4
Slide 5
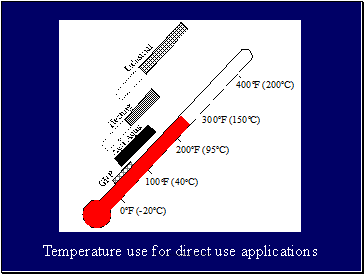
Temperature use for direct use applications
Slide 6
Advantages of Direct-Use of Geothermal Energy
Can use low- to intermediate temperature resources (<150oC)
These resources are more wide-spread (80 countries)
Direct heat use (no conversion – high efficiency)
Use conventional water-well drilling equipment
Use conventional, off-the-shelf equipment
(allow for temperature and chemistry of fluid)
Minimum start-up-time
Slide 7
Advantages of Direct-Use of Geothermal Energy
Can be used on a small scale (“mom and pop operation”)
Individual home
Single greenhouse
Single aquaculture pond
Can also be large scale operation
District heating
Food, lumber and mineral ore drying
Slide 8
Slide 9
Equipment (1)
Often necessary to isolate geothermal fluid to prevent corrosion or scaling
Care taken to prevent oxygen from entering system
Dissolved gases and minerals (boron, arsenic, hydrogen sulfide, etc.) May be harmful to plants and animals
Slide 10
Equipment (2)
Downhole and circulation pumps
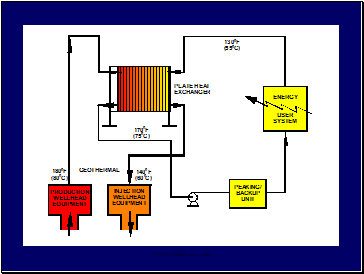
Heat exchangers
Transmission and distribution pipelines
Heat extraction equipment
Peaking or back-up plants
Fluid disposal system
Typical equipment includes:
Slide 11
Contents
- World Wide Direct Utilization
- Advantages of Direct-Use of Geothermal Energy
- Wells Pumps
- Heat Exchangers
- Space Conditioning
- District Heating – Examples
- Agribusiness Applications
- Refrigeration
- Heat Pumps
- Industrial Applications
Last added presentations
- Gravitation
- Space Radiation
- Friction
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Mechanics Lecture
- Soil and Plant Nutrition