Newton’s third law of motionPage
1
1
Slide 1
This lecture will help you understand:
Forces and Interactions
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Summary of Newton’s Laws
Vectors
Slide 2
Forces and Interactions
Interaction
is between one thing and another.
requires a pair of forces acting on two objects.
Example: interaction of hand and wall pushing on each other
Force pair—you push on wall; wall pushes on you.
Slide 3
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first.
Slide 4
A soccer player kicks a ball with 1500 N of force. The ball exerts a reaction force against the player’s foot of
A. somewhat less than 1500 N.
1500 N.
somewhat more than 1500 N.
None of the above.
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
CHECK YOUR NEIGHBOR
Slide 5
A soccer player kicks a ball with 1500 N of force. The ball exerts a reaction force against the player’s foot of
A. somewhat less than 1500 N.
1500 N.
somewhat more than 1500 N.
None of the above.
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
CHECK YOUR ANSWER
Slide 6
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Action and reaction forces
one force is called the action force; the other force is called the reaction force.
are co-pairs of a single interaction.
neither force exists without the other.
are equal in strength and opposite in direction.
always act on different objects.
Slide 7
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Reexpression of Newton’s third law: To every action there is always an opposed equal reaction.
Example: Tires of car push back against the road while the road pushes the tires forward.
Slide 8
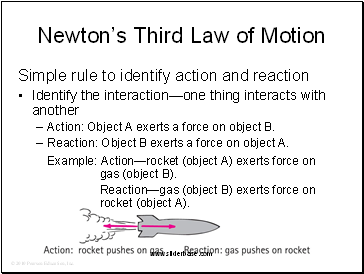
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Simple rule to identify action and reaction
Identify the interaction—one thing interacts with another
Action: Object A exerts a force on object B.
Reaction: Object B exerts a force on object A.
Example: Action—rocket (object A) exerts force on gas (object B).
Reaction—gas (object B) exerts force on rocket (object A).
Slide 9
When you step off a curb, Earth pulls you downward. The reaction to this force is
Contents
Last added presentations
- Waves & Sound
- Solar Energy
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Mechanics Lecture
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Newton’s third law of motion