Wave OpticsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Contents
Coherence and Conditions for Interference
The Michelson Interferometer
Thin-Film Interference
Light through a Single Slit: Qualitative Behavior
Double-Slit Interference: Young’s Experiment of Light from a Single Slit
Diffraction Gratings
Optical Resolution and the Rayleigh Criterion
Why Is the Sky Blue?
Slide 2
Coherence and Conditions for Interference
Wave Optics
The field of wave optics studies the properties of light that depend on its wave nature
Originally light was thought to be a particle and that model successfully explained the phenomena discussed in geometric optics
Maxwell’s theory of electromagnetism convinced physicists that light was a wave
When discussing image characteristics over distances much greater than the wavelength, geometric optics is extremely accurate
When dealing with sizes comparable to or smaller than the wavelength, wave optics is required
Slide 3
Interference
One property unique to waves is interference
Interference of sound waves can be produced by two speakers
Constructive Interference
When the waves are in phase, their maxima occur at the same time at a given point in space
The total wave displacement at the listener’s location is the sum of the displacements of the two individual waves
If two waves are in phase, the sum of their displacements is large
Slide 4
Destructive Interference
The maximum of one wave can coincide with the minimum of the other wave
These waves are out of phase
The interference is destructive when the waves are out of phase
If the waves are 180° out of phase, the sum of the displacements of the two waves is zero
Slide 5
General conditions for interference.
Two waves can interfere if all the following conditions are met.
1. Two or more interfering waves travel through different regions of space over at least part of their propagation from source to destination.
2. The waves are brought together at a common point.
3. The waves must have the same frequency and must also have a fixed phase relationship. Thus, over a given distance or time interval the phase difference between the waves remains constant. Such waves are called coherent.
Slide 6
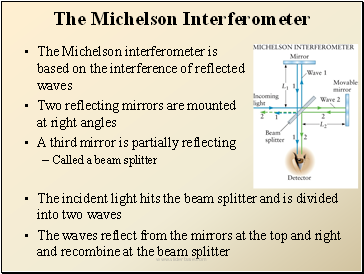
The Michelson Interferometer
The Michelson interferometer is based on the interference of reflected waves
Two reflecting mirrors are mounted at right angles
Contents
- Coherence and Conditions for Interference
- General conditions for interference.
- The Michelson Interferometer
- Thin-Film Interference
- Light through a Single Slit: Qualitative Behavior
- Single-Slit Diffraction
- Double-Slit Interference: Young’s Experiment of Light from a Single Slit
- Single-Slit Diffraction: Interference
- Diffraction Gratings
- Optical Resolution and the Rayleigh Criterion
- Why Is the Sky Blue?
Last added presentations
- Space Radiation
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Buoyancy
- Friction
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things