Ionic Compound NomenclaturePage
1
1
Slide 1
Ionic Compound Formulas
Slide 2
Ions
Cation: A positive ion
Mg2+, NH4+
Anion: A negative ion
Cl-, SO42-
Slide 3
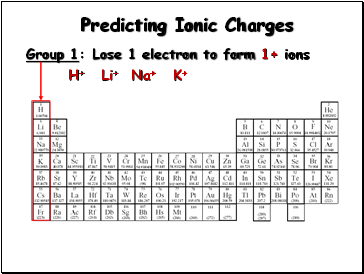
Predicting Ionic Charges
Group 1:
Lose 1 electron to form 1+ ions
H+
Li+
Na+
K+
Slide 4
Predicting Ionic Charges
Group 2:
Loses 2 electrons to form 2+ ions
Be2+
Mg2+
Ca2+
Sr2+
Ba2+
Slide 5
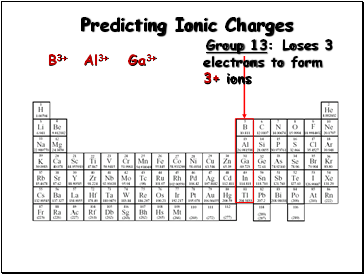
Predicting Ionic Charges
Group 13:
Loses 3
electrons to form
3+ ions
B3+
Al3+
Ga3+
Slide 6
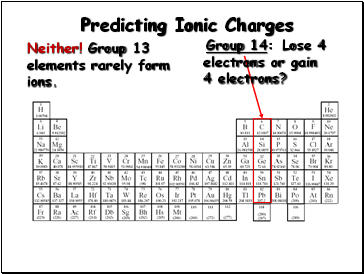
Predicting Ionic Charges
Group 14:
Lose 4
electrons or gain
4 electrons?
Neither! Group 13 elements rarely form ions.
Slide 7
Predicting Ionic Charges
Group 15:
Gains 3
electrons to form
3- ions
N3-
P3-
As3-
Nitride
Phosphide
Arsenide
Slide 8
Predicting Ionic Charges
Group 16:
Gains 2
electrons to form
2- ions
O2-
S2-
Se2-
Oxide
Sulfide
Selenide
Slide 9
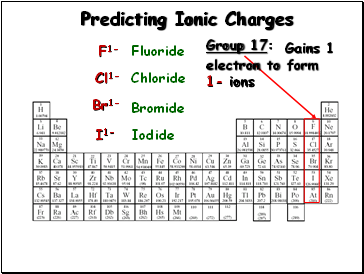
Predicting Ionic Charges
Group 17:
Gains 1
electron to form
1- ions
F1-
Cl1-
Br1-
Fluoride
Chloride
Bromide
I1-
Iodide
Slide 10
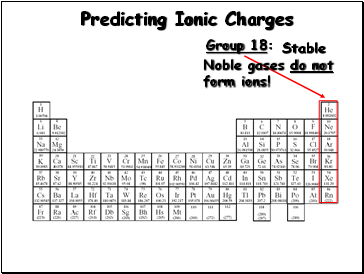
Predicting Ionic Charges
Group 18:
Stable Noble gases do not form ions!
Slide 11
Predicting Ionic Charges
Groups 3 - 12:
Many transition elements
have more than one possible oxidation state.
Iron(II) = Fe2+
Iron(III) = Fe3+
Slide 12
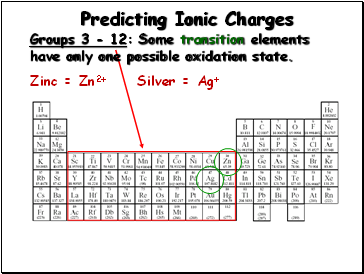
Predicting Ionic Charges
Groups 3 - 12:
Some transition elements
have only one possible oxidation state.
Zinc = Zn2+
Silver = Ag+
Slide 13
Writing Ionic Compound Formulas
Example: Barium nitrate
1. Write the formulas for the cation and anion, including CHARGES!
Ba2+
NO3-
2. Check to see if charges are balanced.
Contents
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants