Endocrine and nervous systemPage
1
1
Slide 1
The Endocrine System
Communication
Chemical
Main Function:
It releases hormones into the blood to signal other cells to behave in certain ways. It is a slow but widespread form of communication.
Slide 2
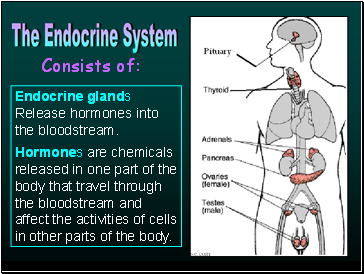
Endocrine glands Release hormones into the bloodstream.
Hormones are chemicals released in one part of the body that travel through the bloodstream and affect the activities of cells in other parts of the body.
Consists of:
The Endocrine System
Slide 3
Pituitary Gland
Function: It secretes nine hormones that directly regulate many body functions and controls functions of other glands.
Disorders: To much growth hormones (GH) in early childhood can result in a condition called gigantism. To little GH can result in Pituitary Dwarfism.
Robert
Wadlow
Slide 4
Thyroid Gland
Function: plays a major role in regulation the body’s metabolism.
Disorders: If the Thyroid Gland produces to much Thyroxin, it can cause a condition known as Hyperthyroidism. If to little thyroxin produces it is called Hypothyroidism.
Slide 5
Pancreas
Function: The Insulin and Glycogen in the Pancreas help to keep the level of glucose in the blood stable.
Disorders: When the Pancreas fails to produce or properly use Insulin, it can cause a condition known as Diabetes Mellitus.
Slide 6
Adrenal Gland
Functions:
-The adrenal glands release Adrenaline in the body that helps prepare for and deal with stress.
-Also regulates kidney function.
Slide 7
Ovaries
Functions:
Pair of reproductive organs found in women that produce eggs.
Also secrete estrogen and progesterone, which control ovulation and menstruation.
Slide 8
Testes
Functions:
Pair of reproductive glands that produces sperm.
Also secrete Testosterone to give the body its masculine characteristics.
Slide 9
Interaction of Glands
The hypothalamus is located in the brain and controls the release of hormones from the pituitary gland. It is an important link between the endocrine and nervous systems.
http://www.biocfarm.unibo.it/aunsnc/images/3D%20Objects/Hypothalamus.gif
Contents
- The Endocrine System
- Pituitary Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Pancreas
- Adrenal Gland
- Ovaries
- Testes
- The Nervous System
- Parts of a Neuron
- Sensory Neuron
- Motor Neurons
- Central Nervous System
Last added presentations
- Buoyancy
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Health Physics
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Newton’s laws of motion