Electrical CircuitsPage
1
1
Slide 1
S.MORRIS 2006
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
Slide 2
The Cell
The cell stores chemical energy and transfers it to electrical energy when a circuit is connected.
When two or more cells are connected together we call this a Battery.
The cells chemical energy is used up pushing a current round a circuit.
Slide 3
What is an electric current?
An electric current is a flow of microscopic particles called electrons flowing through wires and components.
+
-
In which direction does the current flow?
from the Negative terminal to the Positive terminal of a cell.
Slide 4
Simple circuits
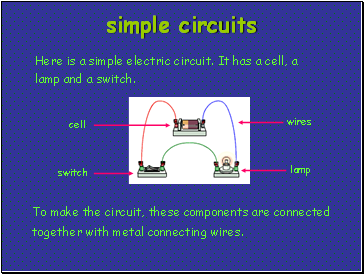
Here is a simple electric circuit. It has a cell, a lamp and a switch.
To make the circuit, these components are connected together with metal connecting wires.
cell
lamp
switch
wires
Slide 5
simple circuits
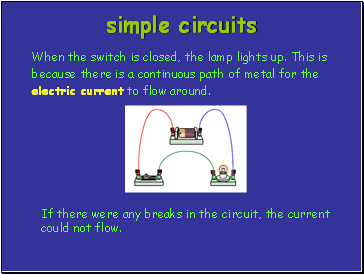
When the switch is closed, the lamp lights up. This is because there is a continuous path of metal for the electric current to flow around.
If there were any breaks in the circuit, the current could not flow.
Slide 6
Circuit diagram
cell
switch
lamp
wires
Scientists usually draw electric circuits using symbols;
Slide 7
circuit diagrams
In circuit diagrams components are represented by the following symbols;
cell
battery
switch
lamp
motor
ammeter
voltmeter
buzzer
resistor
variable resistor
Slide 8
Types of circuit
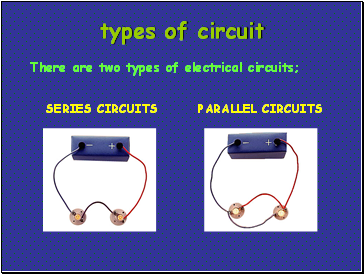
There are two types of electrical circuits;
SERIES CIRCUITS
PARALLEL CIRCUITS
Slide 9
Series circuits
The components are connected end-to-end, one after the other.
They make a simple loop for the current to flow round.
If one bulb ‘blows’ it breaks the whole circuit and all the bulbs go out.
Slide 10
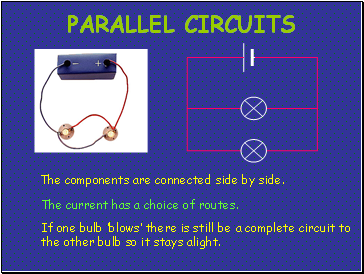
Parallel circuits
The current has a choice of routes.
The components are connected side by side.
If one bulb ‘blows’ there is still be a complete circuit to the other bulb so it stays alight.
Slide 11
Measuring current
Contents
- The Cell
- What is an electric current?
- Simple circuits
- Circuit diagram
- Types of circuit
- Series circuits
- Parallel circuits
- Measuring current
- Measuring voltage
- Measuring current & voltage
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Waves & Sound
- Health Physics
- Newton's Laws
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Thermal Energy