Multiplying DecimalsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Multiplying Decimals
Slide 2
Example: 5.63 x 3.7
5.63
3.7
x
1
2
4
4
39
0
9
8
1
16
+
1
3
1
8
1
0
1
2
two
one
three
.
Slide 3
To Multiply
You do not line up the factors by the decimal.
Instead, place the number with more digits on top.
Line up the other number underneath, at the right.
Multiply
Count the number of decimal places (from the right) in each factor.
Use the total number of decimal places in your two factors to place the decimal in your product.
Slide 4
Example: 0.53 x 2.618
2.618 has more digits (4) than 0.53 (3), so it goes on top.
2.618
0.53
x
4
2
5
8
1
7
0
0
4
9
0
3
13
00
0
0
0
0
+
4
5
7
1
8
3
1
Decimal Places
three
two
five
.
Slide 5
Multiplying Decimals
5.82
0.41
2 decimal places
2 decimal places
5 8 2
2 3 2 8
4 decimal places
2.3 8 6 2
1
2
3
4
Slide 6
6.45
18
2 decimal places
0 decimal places
5160
645
116.10
Multiplying Decimals
2 decimal places
ANSWER
6.45 18 = 116.1
Slide 7
6.45
18
2 decimal places
0 decimal places
5160
645
116.10
1.273
0.06
3 decimal places
2 decimal places
7638
0.0
5 decimal places
Multiplying Decimals
2 decimal places
Slide 8
Try This: 6.5 x 15.3
15.3
6.5
x
5
1
6
2
7
0
8
1
1
3
9
+
5
4
1
9
9
one
one
two
.
Slide 9
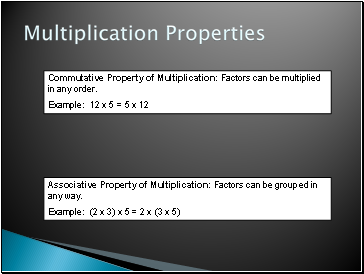
Multiplication Properties
Commutative Property of Multiplication: Factors can be multiplied in any order.
Example: 12 x 5 = 5 x 12
Associative Property of Multiplication: Factors can be grouped in any way.
Example: (2 x 3) x 5 = 2 x (3 x 5)
Slide 10
If a Decimal number is multiplied by 10,100, 1000 etc., the decimal shifts to the right side according to the number of Zeroes.
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Waves & Sound
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Friction
- Newtons third law of motion
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort