Periodic BehaviorPage
1
1
Slide 1
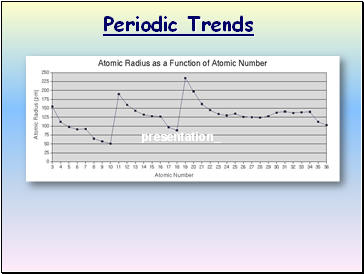
Periodic Trends
Slide 2
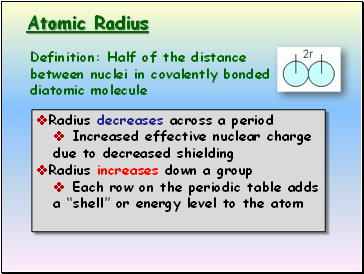
Atomic Radius
Definition: Half of the distance between nuclei in covalently bonded diatomic molecule
Radius decreases across a period
Increased effective nuclear charge due to decreased shielding
Radius increases down a group
Each row on the periodic table adds a “shell” or energy level to the atom
Slide 3
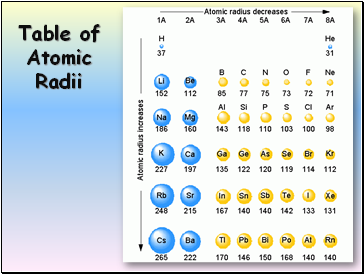
Table of Atomic Radii
Slide 4
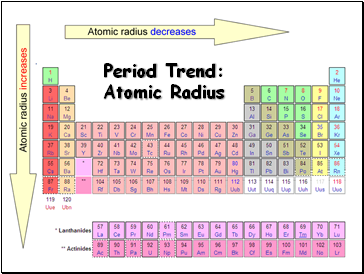
Period Trend: Atomic Radius
Slide 5
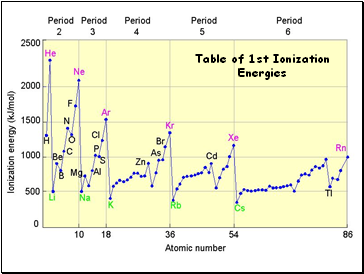
Ionization Energy
Increases for successive electrons taken from the same atom
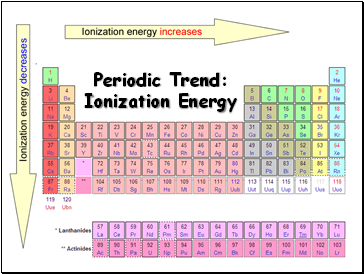
Tends to increase across a period
Electrons in the same quantum level do not shield as effectively as electrons in inner levels
Irregularities at half filled and filled sublevels due to extra repulsion of electrons paired in orbitals, making them easier to remove
Tends to decrease down a group
Outer electrons are farther from the nucleus and easier to remove
Definition: the energy required to remove an electron from an atom
Slide 6
Ionization Energy: the energy required to remove an electron from an atom
Increases for successive electrons taken from the same atom
Tends to increase across a period
Electrons in the same quantum level do not shield as effectively as electrons in inner levels
Irregularities at half filled and filled sublevels due to extra repulsion of electrons paired in orbitals, making them easier to remove
Tends to decrease down a group
Outer electrons are farther from the nucleus
Slide 7
Table of 1st Ionization Energies
Slide 8
Periodic Trend: Ionization Energy
Slide 9
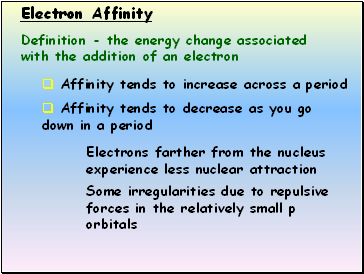
Electron Affinity
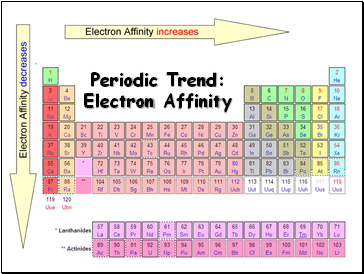
Affinity tends to increase across a period
Affinity tends to decrease as you go down in a period
Electrons farther from the nucleus experience less nuclear attraction
Some irregularities due to repulsive forces in the relatively small p orbitals
Definition - the energy change associated with the addition of an electron
Slide 10
Periodic Trend: Electron Affinity
Slide 11
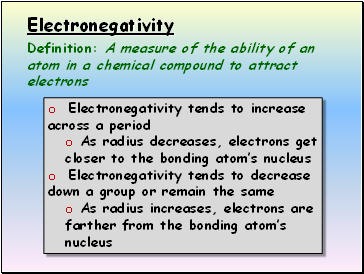
Electronegativity
1 2
Contents
- Atomic Radius
- Table of Atomic Radii
- Period Trend: Atomic Radius
- Ionization Energy
- Periodic Trend: Ionization Energy
- Electron Affinity
- Periodic Trend: Electron Affinity
- Electronegativity
- Periodic Table of Electronegativities
- Periodic Trend: Electronegativity
- Summary of Periodic Trends
- Ionic Radii
- Table of Ion Sizes
Last added presentations
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Solar Energy
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Newton's Laws
- Buoyancy
- Motion