Polarization of Light from Basics to InstrumentsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Polarization of Light: from Basics to Instruments (in less than 100 slides)
N. Manset
CFHT
Slide 2
Introduction
Part I: Different polarization states of light
Part II: Stokes parameters, Mueller matrices
Part III: Optical components for polarimetry
Part IV: Polarimeters
Part V: ESPaDOnS
Slide 3
Different polarization states of light
Light as an electromagnetic wave
Mathematical and graphical descriptions of polarization
Linear, circular, elliptical light
Polarized, unpolarized light
Slide 4
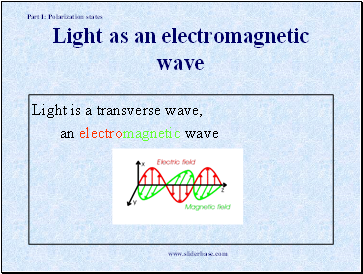
Light as an electromagnetic wave
Light is a transverse wave,
an electromagnetic wave
Part I: Polarization states
Slide 5
Mathematical description of the EM wave
Light wave that propagates in the z direction:
Part I: Polarization states
Slide 6
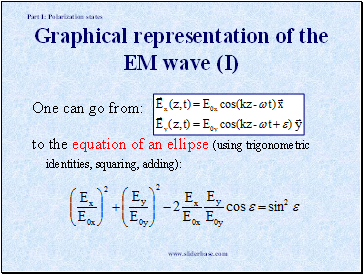
Graphical representation of the EM wave (I)
One can go from:
to the equation of an ellipse (using trigonometric identities, squaring, adding):
Part I: Polarization states
Slide 7
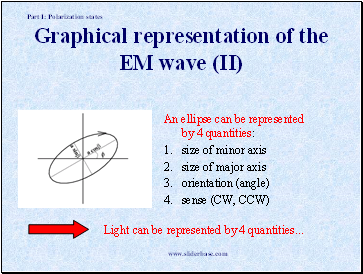
Graphical representation of the EM wave (II)
An ellipse can be represented by 4 quantities:
size of minor axis
size of major axis
orientation (angle)
sense (CW, CCW)
Light can be represented by 4 quantities .
Part I: Polarization states
Slide 8
Vertically polarized light
If there is no amplitude in x (E0x = 0), there is only one component, in y (vertical).
Part I: Polarization states, linear polarization
Slide 9
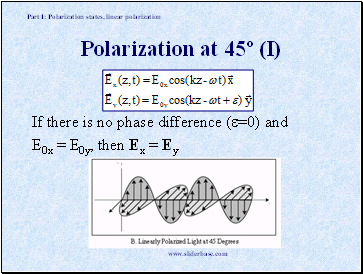
Polarization at 45º (I)
If there is no phase difference (=0) and
E0x = E0y, then Ex = Ey
Part I: Polarization states, linear polarization
Slide 10
Polarization at 45º (II)
Part I: Polarization states, linear polarization
Slide 11
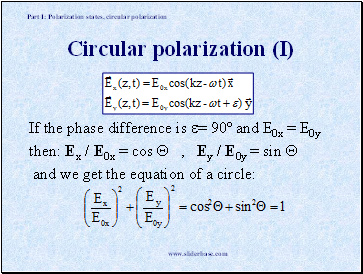
Circular polarization (I)
If the phase difference is = 90º and E0x = E0y
then: Ex / E0x = cos , Ey / E0y = sin
and we get the equation of a circle:
Contents
- Introduction
- Different polarization states of light
- Stokes parameters and Mueller matrices
- Optical components for polarimetry
- Polarimeters
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Madame Marie Curie
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Health Physics
- Newton's laws of motion