Angiosperm Reproduction and BiotechnologyPage
1
1
Slide 1
Angiosperm Flowers
Angiosperm flowers can attract pollinators using visual cues and volatile chemicals.
Many angiosperms reproduce sexually and asexually.
Symbiotic relationships are common between plants and other species.
Since the beginning of agriculture, plant breeders have genetically manipulated traits of wild angiosperm species by artificial selection.
Slide 2
Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle
Alternation of Generations:
Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis 2n ---> n these spores (n) grow into haploid (n) gametophytes.
Gametophytes produce haploid (n) gametes by mitosis fertilization of gametes produces a zygote = sporophyte cell (2n).
Slide 3
In angiosperms, the sporophyte is the dominant generation, the large plant that we see.
The gametophytes are reduced in size and depend on the sporophyte for nutrients.
The angiosperm life cycle is characterized by “three Fs”: flowers, double fertilization, and fruits.
Slide 4
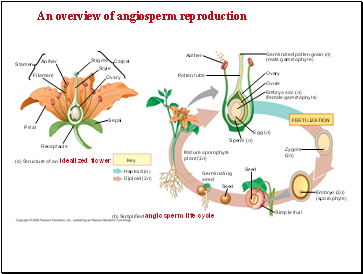
Stamen
Anther
Filament
Stigma
Carpel
Style
Ovary
Anther
Pollen tube
Germinated pollen grain (n)
(male gametophyte)
Ovary
Ovule
Embryo sac (n)
(female gametophyte)
Egg (n)
Sperm (n)
Zygote
(2n)
Seed
Seed
Embryo (2n)
(sporophyte)
Simple fruit
Germinating
seed
Mature sporophyte
plant (2n)
(b) Simplified angiosperm life cycle
Key
Receptacle
Sepal
Petal
(a) Structure of an idealized flower
Haploid (n)
Diploid (2n)
FERTILIZATION
An overview of angiosperm reproduction
Slide 5
Stamen
Anther
Filament
Stigma
Carpel
Style
Ovary
Receptacle
Sepal
Petal
Structure of an idealized flower
Slide 6
Anther
pollen
Pollen tube
Pollination
Germinated pollen grain (n)
(male gametophyte)
Ovary
Ovule : Double Fertilization
Embryo sac (n)
(female gametophyte)
Egg (n)
Sperm (n)
Endosperm
(3n)
Zygote
(2n)
Seed
Seed
Embryo (2n)
(sporophyte)
Simple fruit
Germinating
seed
Mature sporophyte
plant (2n)
Angiosperm Life Cycle
Key
Haploid (n)
Diploid (2n)
FERTILIZATION
Slide 7
Flower Structure and Function
Contents
- Angiosperm Flowers
- Alternation of Generations:
- Flower Structure and Function
- Development of Male Gametophytes in Pollen Grains
- Development of Female Gametophytes (Embryo Sacs)
- Pollination
- Double Fertilization
- Seed Development, Form, and Function
- Endosperm Development
- Structure of the Mature Seed
- Fruit Form and Function
- Plants reproduce sexually, asexually, or both
- Mechanisms of Asexual Reproduction
- Mechanisms That Prevent Self-Fertilization
- Vegetative Propagation and Agriculture
- Humans modify crops by breeding and genetic engineering
- Plant Breeding
- Plant Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering
- The Debate over Plant Biotechnology
- You should now be able to:
Last added presentations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Static and Kinetic Friction