An Introduction to MetabolismPage
1
1
Slide 1
The Energy of Life
The living cell is a miniature chemical factory where thousands of reactions occur
The cell extracts energy and applies energy to perform work
Some organisms even convert energy to light, as in bioluminescence
Slide 2
Fig. 8-1
Slide 3
Concept 8.1: An organismís metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics
Metabolism is the totality of an organismís chemical reactions
Metabolism is an emergent property of life that arises from interactions between molecules within the cell
Slide 4
Organization of the Chemistry of Life into Metabolic Pathways
A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and ends with a product
Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme
Slide 5
Fig. 8-UN1
Enzyme 1
Enzyme 2
Enzyme 3
D
C
B
A
Reaction 1
Reaction 3
Reaction 2
Starting
molecule
Product
Slide 6
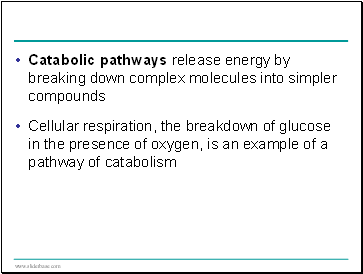
Catabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds
Cellular respiration, the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen, is an example of a pathway of catabolism
Slide 7
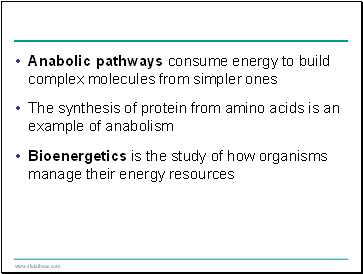
Anabolic pathways consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones
The synthesis of protein from amino acids is an example of anabolism
Bioenergetics is the study of how organisms manage their energy resources
Slide 8
Forms of Energy
Energy is the capacity to cause change
Energy exists in various forms, some of which can perform work
Slide 9
Kinetic energy is energy associated with motion
Heat (thermal energy) is kinetic energy associated with random movement of atoms or molecules
Potential energy is energy that matter possesses because of its location or structure
Chemical energy is potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction
Energy can be converted from one form to another
Animation: Energy Concepts
Slide 10
Fig. 8-2
Climbing up converts the kinetic
energy of muscle movement
Contents
- The Energy of Life
- Organization of the Chemistry of Life into Metabolic Pathways
- Forms of Energy
- The Laws of Energy Transformation
- The First Law of Thermodynamics
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics
- Biological Order and Disorder
- Free-Energy Change, ∆G
- Free Energy, Stability, and Equilibrium
- Free Energy and Metabolism
- Equilibrium and Metabolism
- The Structure and Hydrolysis of ATP
- How ATP Performs Work
- The Regeneration of ATP
- The Activation Energy Barrier
- How Enzymes Lower the EA Barrier
- Substrate Specificity of Enzymes
- Catalysis in the Enzymeís Active Site
- Effects of Local Conditions on Enzyme Activity
- Cofactors
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Allosteric Regulation of Enzymes
- Allosteric Activation and Inhibition
- Identification of Allosteric Regulators
- Feedback Inhibition
- Specific Localization of Enzymes Within the Cell
- You should now be able to
Last added presentations
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Gravitation
- Newtonís Laws of Motion
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Solar Thermal Energy