PH Scale and CalculationsPage
1
1
Slide 1
pH Scale and Calculations
Chapter 14
Page 565-574
Slide 2
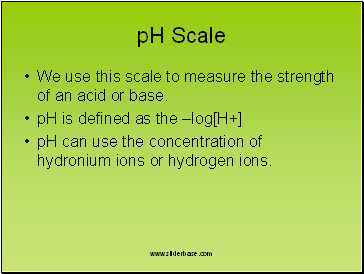
pH Scale
We use this scale to measure the strength of an acid or base.
pH is defined as the –log[H+]
pH can use the concentration of hydronium ions or hydrogen ions.
Slide 3
pH Scale
Acid
Base
0
7
14
Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry 2002, page 515
Slide 4
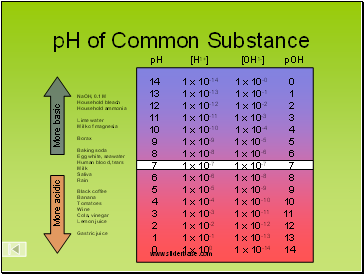
pH of Common Substances
Timberlake, Chemistry 7th Edition, page 335
Slide 5
pH of Common Substance
14 1 x 10-14 1 x 10-0 0
13 1 x 10-13 1 x 10-1 1
12 1 x 10-12 1 x 10-2 2
11 1 x 10-11 1 x 10-3 3
10 1 x 10-10 1 x 10-4 4
9 1 x 10-9 1 x 10-5 5
8 1 x 10-8 1 x 10-6 6
6 1 x 10-6 1 x 10-8 8
5 1 x 10-5 1 x 10-9 9
4 1 x 10-4 1 x 10-10 10
3 1 x 10-3 1 x 10-11 11
2 1 x 10-2 1 x 10-12 12
1 1 x 10-1 1 x 10-13 13
0 1 x 100 1 x 10-14 14
NaOH, 0.1 M
Household bleach
Household ammonia
Lime water
Milk of magnesia
Borax
Baking soda
Egg white, seawater
Human blood, tears
Milk
Saliva
Rain
Black coffee
Banana
Tomatoes
Wine
Cola, vinegar
Lemon juice
Gastric juice
More basic
More acidic
pH [H1+] [OH1-] pOH
7 1 x 10-7 1 x 10-7 7
Slide 6
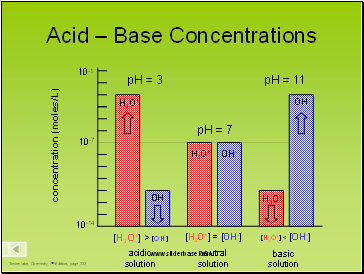
Acid – Base Concentrations
pH = 3
pH = 7
pH = 11
OH-
H3O+
OH-
OH-
H3O+
H3O+
[H3O+] = [OH-]
[H3O+] > [OH-]
[H3O+] < [OH-]
acidic
solution
neutral
solution
basic
solution
concentration (moles/L)
10-14
10-7
10-1
Timberlake, Chemistry 7th Edition, page 332
Slide 7
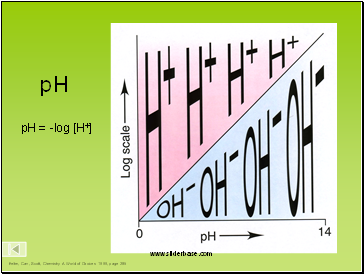
pH
pH = -log [H+]
Kelter, Carr, Scott, Chemistry A World of Choices 1999, page 285
Slide 8
Self-Ionization Of Water
Even the purest of water conducts electricity. This is due to the fact that water self-ionizes, that is, it creates a small amount of H3O+ and OH-.
H2O + H2O º H3O+ + OH-
Kw = [H3O+][OH-]
Kw - ion product of water
Kw = 1.0 x 10-14 at 25 oC
This equilibrium constant is very important because it applies to all aqueous solutions - acids, bases, salts, and non-electrolytes - not just to pure water.
Slide 9
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Mechanics Lecture
- Newton's Laws
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Friction
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Heat-Energy on the Move