MineralsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Minerals
Slide 2
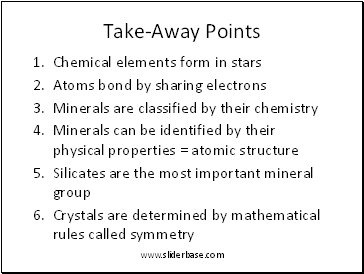
Take-Away Points
Chemical elements form in stars
Atoms bond by sharing electrons
Minerals are classified by their chemistry
Minerals can be identified by their physical properties = atomic structure
Silicates are the most important mineral group
Crystals are determined by mathematical rules called symmetry
Slide 3
Composition of the Sun
1. Chemical elements form in stars
Slide 4
Composition of the Sun
Abundance of Light Elements
Rarity of Lithium, Beryllium, Boron
Preference for Even Numbers
Abundance peak at Iron, trailing off after
1. Chemical elements form in stars
Slide 5
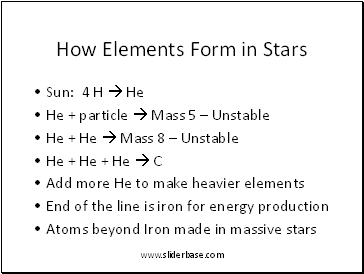
How Elements Form in Stars
Sun: 4 H He
He + particle Mass 5 – Unstable
He + He Mass 8 – Unstable
He + He + He C
Add more He to make heavier elements
End of the line is iron for energy production
Atoms beyond Iron made in massive stars
1. Chemical elements form in stars
Slide 6
What are Planets Made of?
Same material as Sun
Minus the elements that remain mostly in gases
We find this pattern in a certain class of meteorites
1. Chemical elements form in stars
Slide 7
Chondrites
1. Chemical elements form in stars
Slide 8
The Earth’s Crust looks Very Different
1. Chemical elements form in stars
Slide 9
Composition of the Crust
1. Chemical elements form in stars
Slide 10
Minerals are the Chemicals that make up the Earth
Naturally Occurring
Inorganic
Chemical Compounds
About 5000 Known
200 Common
20 Rock-Forming
Slide 11
Atomic Bonding
1. IONS
2. Atoms bond by sharing electrons
Slide 12
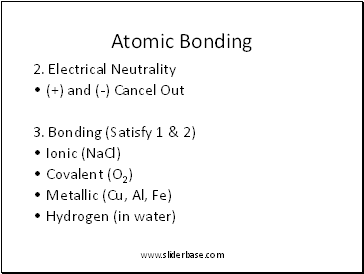
Atomic Bonding
2. Electrical Neutrality
(+) and (-) Cancel Out
3. Bonding (Satisfy 1 & 2)
Ionic (NaCl)
Contents
- Take-Away Points
- Composition of the Sun
- How Elements Form in Stars
- What are Planets Made of?
- Minerals are the Chemicals that make up the Earth
- Summary of Bonding
- Naming minerals
- Identifying Minerals
- Color
- Hardness
- Density
- Luster
- Cleavage
- Identifying Minerals
- Unit Cells
Last added presentations
- Gravitation
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Upcoming Classes
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Health Physics
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Waves & Sound