Balancing Chemical Equations. Balancing redox equationsPage
1
1
Slide 1
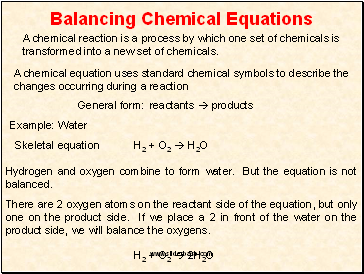
Balancing Chemical Equations
A chemical reaction is a process by which one set of chemicals is
transformed into a new set of chemicals.
A chemical equation uses standard chemical symbols to describe the changes occurring during a reaction
General form: reactants products
Example: Water
Skeletal equation
H2 + O2 H2O
Hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water. But the equation is not balanced.
There are 2 oxygen atoms on the reactant side of the equation, but only one on the product side. If we place a 2 in front of the water on the product side, we will balance the oxygens.
H2 + O2 2H2O
Slide 2
We now need to balance the hydrogens
Place a 2 before the hydrogens on the reactant side of the equation
2H2 + O2 2H2O
Balanced
Note: Diatomic molecules
Equation for formation of water included hydrogens and oxygens with subscript 2.
Other elements which occur in this way are Nitrogen, Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine and Iodine.
These elements occur naturally as diatomic (meaning 2 atoms) molecules
The stoichiometric coefficients multiplying the chemical formulas tell you the relative numbers of moles of each substance that reacts or is produced in a chemical reaction.
Therefore, we can conclude from the balanced equation for water that 2 moles of hydrogen and one mol of oxygen combine to form water.
Slide 3
A chemical equation may also tell you what physical state the reactants and products are in. The following state symbols are used:
s (solid)
l (liquid)
g (gas)
aq (aqueous solution)
These are found as subscripts after each reactant and product.
Example
Balance the following equation:
Na(s) + H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
Step 1: How many atoms of each element are present on the reactant and product side?
Reactants
Products
Na
H
O
1
2
1
Na
H
O
1
3
1
Slide 4
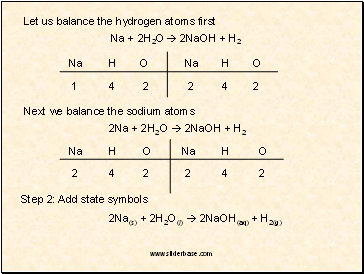
Let us balance the hydrogen atoms first
Na + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2
Na
H
O
Na
H
O
1
4
2
2
4
2
Next we balance the sodium atoms
2Na + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2
Na
H
O
Na
H
O
2
4
2
2
4
2
Step 2: Add state symbols
2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
Slide 5
Questions
Balance the following equations:
(a) P2O5(s) + H2O(l) H3PO4(aq)
Answer: P2O5(s) + 3H2O(l) 2H3PO4(aq)
Contents
- Balancing Chemical Equations
- Balancing redox reactions
- Rules for assigning oxidation numbers (O.N.)
- Defining Oxidising and Reducing agents
- Identifying Oxidising and Reducing Agents
- Balancing redox equations
Last added presentations
- Solar Energy
- Space Radiation
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Newton's laws of motion
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Newton’s third law of motion