Balancing Chemical Equations. Balancing redox equationsPage
7
7
0
-1
-3
0
-4
-1
0
Slide 28
Step 7: Ensure the number of electrons gained equals the number of electrons lost and add the two half reactions together
2I- I2 + 2e-
× 3
2H2O + MnO4- + 3e- MnO2 + 4OH-
× 2
6I- 3I2 + 6e-
4H2O + 2MnO4- + 6e- 2MnO2 + 8OH-
2MnO4- + 6I- + 4H2O 2MnO2 + 3I2 + 8OH-
Balanced
Check to ensure that all atoms and charges are balanced.
Slide 29
Question
Balance the following redox equation which occurs in basic solution
Mn2+ + H2O2 MnO2 + H2O
Step 1: Identify the oxidising and reducing agents and write half reactions
Mn2+ MnO2
Mn2+ : +2
MnO2: Mn +2(-2) = 0
Mn = +4
Mn2+ loses two electrons: it acts as the reducing agent as it is oxidised
Mn2+ MnO2 + 2e- Oxidation reaction
H2O2 H2O
H2O2: 2(+1) + 2O = 0
O = -1
H2O: 2(+1) + O = 0
O = -2
H2O2 gains one electron: it acts as the oxidising agent as it is reduced
H2O2 + e- H2O Reduction reaction
Slide 30
Step 2: Balance each kind of atom other than H and O.
Already balanced in this case
Step 3: Balance the O atoms by using H2O
2H2O + Mn2+ MnO2 + 2e-
H2O2 + e- 2H2O
Step 4: Balance the H atoms by using H+
2H2O + Mn2+ MnO2 + 2e- + 4H+
2H+ + H2O2 + e- 2H2O
Step 5: For each H+ ion, add equal no. of OH- to both sides of equation
2H2O + Mn2+ + 4OH- MnO2 + 2e- + 4H+ + 4OH-
2H2O + Mn2+ + 4OH- MnO2 + 2e- + 4H2O
Mn2+ + 4OH- MnO2 + 2e- + 2H2O
Mn2+ MnO2 + 2e-
H2O2 + e- H2O
Slide 31
2H+ + 2OH- + H2O2 + e- 2H2O + 2OH-
2H2O + H2O2 + e- 2H2O + 2OH-
H2O2 + e- 2OH-
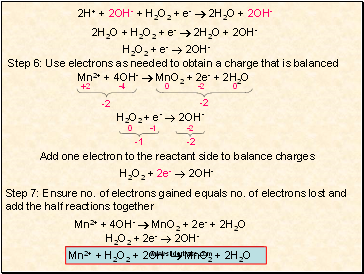
Step 6: Use electrons as needed to obtain a charge that is balanced
Mn2+ + 4OH- MnO2 + 2e- + 2H2O
-2
-2
H2O2 + e- 2OH-
-1
-2
Add one electron to the reactant side to balance charges
H2O2 + 2e- 2OH-
Step 7: Ensure no. of electrons gained equals no. of electrons lost and add the half reactions together
Mn2+ + 4OH- MnO2 + 2e- + 2H2O
H2O2 + 2e- 2OH-
Mn2+ + H2O2 + 2OH- MnO2 + 2H2O
+2
-4
0
-2
0
-2
-1
0
Slide 32
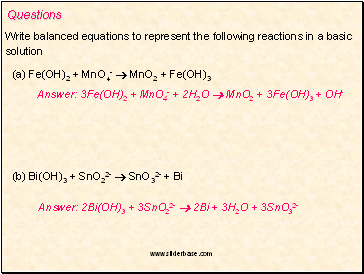
Questions
Write balanced equations to represent the following reactions in a basic
solution
(a) Fe(OH)2 + MnO4- MnO2 + Fe(OH)3
Contents
- Balancing Chemical Equations
- Balancing redox reactions
- Rules for assigning oxidation numbers (O.N.)
- Defining Oxidising and Reducing agents
- Identifying Oxidising and Reducing Agents
- Balancing redox equations
Last added presentations
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Newton's laws of motion
- Waves & Sound
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire