A History of AstronomyPage
1
1
Slide 1

A History of Astronomy
Slide 2

Ancient Astronomy
“Ancient” means from time long past, especially before the end of the Western Roman Empire in 476 A.D.
Many ancient peoples, including in ancient China and India, made detailed observations about the objects in the sky
These observations were useful in making calendars, which helped in yearly planning, and were also part of many religions
Slide 3

Is the solar system geocentric or heliocentric?
“geo” = earth, “helio” = sun, “centric” = centered, so “geocentric” means “earth-centered” and “heliocentric” means “sun-centered”
Most ancient Greek astronomers believed that the earth was the center of the solar system and the universe, with everything orbiting it, which is called a “geocentric” model or system
We now know that the earth orbits the sun, which is called a “heliocentric” model
Slide 4

Ancient Greek Astronomy
• Most ancient Greeks believed that all astronomical objects were perfect, unchanging spheres and orbited in perfect circles around the earth, following different physical laws from those on Earth
• These ideas were believed by most people until Copernicus, Kepler, and Galileo disproved them more than 1000 years later
• Although they had many wrong ideas about the solar system, the ancient Greeks made many important astronomical discoveries
Slide 5

Astronomy in the Middle Ages
In European history, the Middle Ages lasted from about 500 A.D. to about 1500 A.D. (between antiquity and the modern period)
In Europe, astronomy (and knowledge in general) did not gain much during the Middle Ages, and so it has been called “The Dark Ages”
Slide 6

Nicholas Copernicus (1473 - 1543)
The publication of Copernicus' book, On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres, just before his death in 1543, is considered a major event in the history of science
It argued for the heliocentric model based on the observed backward motion of Mars
Slide 7
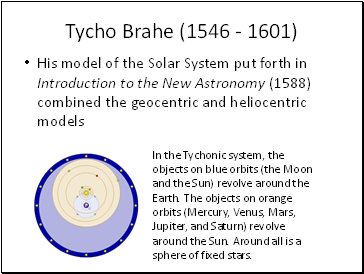
Tycho Brahe (1546 - 1601)
His model of the Solar System put forth in Introduction to the New Astronomy (1588) combined the geocentric and heliocentric models
Slide 8

Johannes Kepler (1571 - 1630)
Published Astronomia nova in 1609
1 2
Contents
- A History of Astronomy
- Ancient Astronomy
- Ancient Greek Astronomy
- Astronomy in the Middle Ages
- Nicholas Copernicus (1473 - 1543)
- Tycho Brahe (1546 - 1601)
- Johannes Kepler (1571 - 1630)
- Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642)
- Isaac Newton (1642 - 1727)
Last added presentations
- Madame Marie Curie
- Friction
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Waves & Sound
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Newton’s laws of motion
