InfluenzaPage
1
1
Slide 1
Influenza
Ieuan Davies
Slide 2
Signs and Symptoms
Influenza is an acute, viral respiratory infection.
Fever, chills, headache, aches and pains throughout the body, sore throat which may lead to bronchitis or pneumonia.
Vomiting and diarrhoea may also occur.
Many deaths have been attributed to influenza
Slide 3
Influenza Pandemics
A pandemic is a world wide spread of infection occurring in many countries simultaneously.
Flu pandemics occur approximately every thirty years.
Flu pandemics occur because a new strain of the virus emerges for which people have no immunity and there are no vaccines available.
Slide 4
Pandemics
New flu viruses occur due to mutation
Mutation occurs because different strains of influenza virus can exchange genes by infecting different animals
Avian influenza viruses can exchange genes with human influenza viruses creating hybrid strains
Slide 5
1918 - 1919 pandemic
This killed between 20 – 40 million people
Face masks were worn but provided little protection against infection
Slide 6
Cause
The cause of influenza is the influenza virus.
Influenza A, B and C viruses are found
Influenza A viruses are associated with serious illness and pandemics
Slide 7
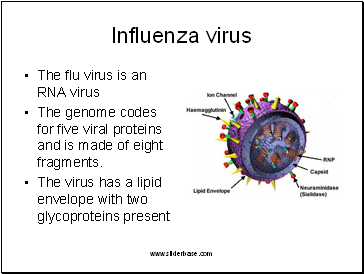
Influenza virus
The flu virus is an RNA virus
The genome codes for five viral proteins and is made of eight fragments.
The virus has a lipid envelope with two glycoproteins present
Slide 8
Flu virus glycoproteins
Haemagglutinin - this glycoprotein plays a part in infection and provides the “H” in the strain type.
Haemagglutinin attaches the virus to cells and allows the viral envelope to fuse with the cell membrane and enter cells.
Neuraminidase – has a mushroom shape, its role is to allow the release of viruses to infect other cells
Slide 9
HN terminolgy
H refers to Haemagglutinin types and each is given a number H1, H2 etc,
Neuraminidase is designated N and different forms are available as well e.g. H5N1 (avian) and H1N1.
Different combinations of H and N glycoproteins give rise to different strains
1 2
Contents
- Signs and Symptoms
- Influenza Pandemics
- Pandemics
- Cause
- Influenza virus
- Flu virus glycoproteins
- HN terminolgy
- Antigenic shift and antigenic drift
- Life cycle of the ‘flu virus
- Transmission
- Prevention
- Immunisation
- Chemotherapy
- Conclusion
Last added presentations
- Motion
- Health Physics
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Sound
- Solar Energy