EyePage
1
1
Slide 1
EYE
The eye is an extension of the brain
Slide 2
Eye brain proxomity
Can you see :
the optic nerve bundle?
Spinal cord?
Slide 3
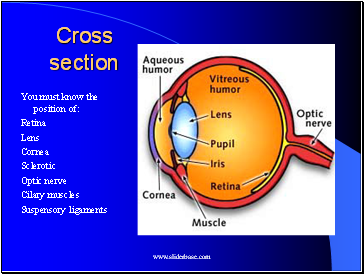
Cross section
You must know the position of:
Retina
Lens
Cornea
Sclerotic
Optic nerve
Cilary muscles
Suspensory ligaments
Slide 4
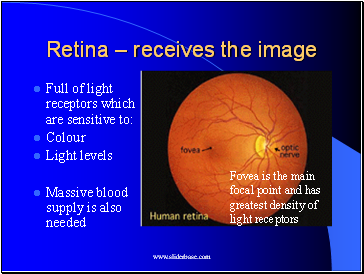
Retina – receives the image
Full of light receptors which are sensitive to:
Colour
Light levels
Massive blood supply is also needed
Fovea is the main focal point and has greatest density of light receptors
Slide 5
Retina receptors
Light receptors are called rods and cone
Slide 6
Focusing on objects
The lens and cornea focus the light on the retina
Slide 7
Focusing
The lens job is to make the rays hit the same point
The red rays will be out of focus
Slide 8
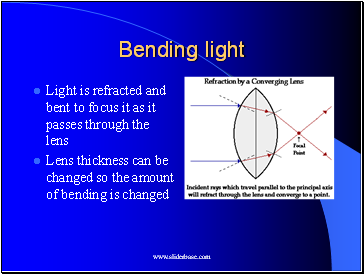
Bending light
Light is refracted and bent to focus it as it passes through the lens
Lens thickness can be changed so the amount of bending is changed
Slide 9
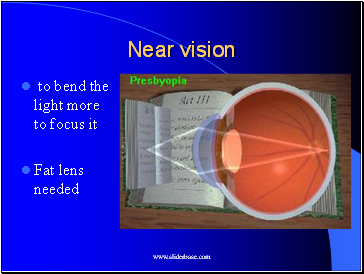
Near vision
to bend the light more to focus it
Fat lens needed
Slide 10
Distance vision
Rays enter the eye closer together
Need less bending
Thinner lens needed
Slide 11
Changing lens thickness
The lens is slightly elastic, its relaxed state is short and fat.
Cilary muscles are attached to the lens, when contracted they pull the lens thin
Slide 12
Controlling light levels
Your eye are very sensitive and can be damaged by harsh light.
Your iris controls light allowed into the eye by changing the size of the pupil
Contents
- Eye brain proxomity
- Cross section
- Retina – receives the image
- Retina receptors
- Focusing on objects
- Focusing
- Bending light
- Near vision
- Distance vision
- Changing lens thickness
- Controlling light levels
Last added presentations
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Friction
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Mechanics Lecture
- History of Modern Astronomy