BloodPage
1
1
Slide 1
Blood
By the end of the lesson you should be able to:
State the composition of Blood
State the function of red blood cells and plasma
Explain the function of haemoglobin in the transport of oxygen
State the function of macrophages and lymphocytes
Slide 2
the average human has 5 litres of blood
it is a transporting fluid
it carries vital substances to all parts of the body
Blood
Slide 3
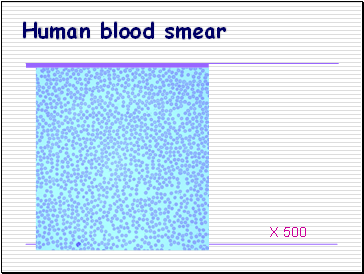
Human blood smear
X 500
Slide 4
plasma (55%)
red blood cells
(5-6-million /ml)
white blood cells
(5000/ml)
platelets
skool blood plasma
Slide 5
x 1000
Slide 6
Plasma
liquid part of blood
plasma transports:-
soluble food molecules
waste products
hormones
antibodies
Slide 7
Red blood cells (RBCs)
transport oxygen
specialised to do this
Also carry some CO2
Slide 8
White blood cells
the bodies “defence”
part of the immune system
much larger than RBCs
far fewer
have a nucleus
4000-13000 per mm3
2 types
phagocytes and lymphocytes
Slide 9
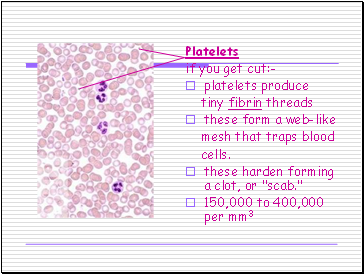
Platelets
if you get cut:-
platelets produce
tiny fibrin threads
these form a web-like
mesh that traps blood
cells.
these harden forming a clot, or "scab."
150,000 to 400,000 per mm3
Slide 10
Red blood cells specialisations
2) no nucleus
extra space inside
3) contain haemoglobin
the oxygen carrying molecule
250million molecules / cell
1) biconcave shape
increases the surface area so more oxygen can be carried
Slide 11
Haemoglobin
gives red blood cells their colour
can carry up to 4 molecules of O2
associates and dissociates with O2
contains iron
Slide 12
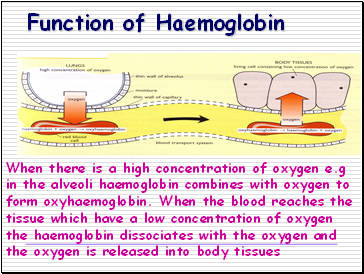
When there is a high concentration of oxygen e.g in the alveoli haemoglobin combines with oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin. When the blood reaches the tissue which have a low concentration of oxygen the haemoglobin dissociates with the oxygen and the oxygen is released into body tissues
1 2
Contents
- Blood
- Human blood smear
- Plasma
- Red blood cells (RBCs)
- White blood cells
- Platelets
- Haemoglobin
- Monocytes
- Phagocytes
- Lymphocyte
- Blood
Last added presentations
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Radiation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Health Physics
- Solar Energy