The History of DNAPage
1
1
Slide 1
The History of DNA
The scientists who discovered Dna
Slide 2
Gregor Mendel
Austrian monk
Born in 1822
In monastery known for
research and teaching
After his death (1884) acknowledgment of his
discoveries in 1900
Known as ďThe Father of Geneticsď
Slide 3
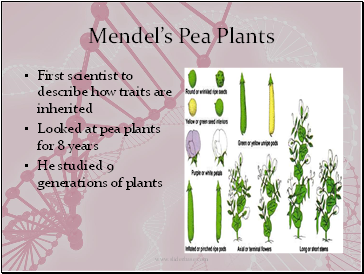
Mendelís Pea Plants
First scientist to describe how traits are inherited
Looked at pea plants for 8 years
He studied 9 generations of plants
Slide 4
Mendelís Observations
He noticed that peas are easy to breed for pure traits and he called the pure strains purebreds.
He developed pure strains of peas for seven different traits (i.e. tall or short, round or wrinkled, yellow or green, etc.)
He crossed these pure strains to produce hybrids.
Slide 5
Mendelís Results
Mendel crossed purebred tall plants with purebred short plants and the first generation plants were all tall.
When these tall offspring were crossed the result was a ratio of 3 tall to 1 short.
Slide 6
The Traits Mendel Looked At
Slide 7
Dominant Trait Rule
Strong Hereditary traits cover weak traits.
Mendel called stronger traits
DOMINANT Ė Represented by CAPITAL LETTER (T)
Mendel called weaker traits
Recessive Ė Represented by lower case letter (t)
Slide 8
Fredrick Griffith
Worked in the 1920ís
Taxonomist Ė a scientist who classifies and names organisms Ė He specialized in pathogens (disease-causing organisms)
Used mice and bacterium (Streptococcus pneumonia) to see if inherited material is passed though DNA or protein.
Slide 9
Oswald Avery
Continued Griffithís work
Identified DNA as the material that passes on the inherited information.
He used large amounts of bacteria and a process of heating and mixing the liquids to extract the nitrogen bases away from the protein
Became worldís first genetic engineer
Slide 10
Erwin Chargaff and his rule
In 1950, biochemist Erwin Chargaff found that the arrangement of nitrogen bases in DNA varied widely,
1 2
Contents
- Gregor Mendel
- Mendelís Pea Plants
- Mendelís Observations
- Mendelís Results
- The Traits Mendel Looked At
- Dominant Trait Rule
- Fredrick Griffith
- Oswald Avery
- Erwin Chargaff and his rule
- Rosalind Franklin (1920-1953)
- James Watson and Francis Crick
Last added presentations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Health Physics
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Mechanics Lecture
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Upcoming Classes