Structure od DNAPage
1
1
Slide 1
AS Biology. Gnetic control of protein structure and function
Genetic control of protein structure and function
Slide 2
AS Biology.
Gnetic control of protein structure and function
The structure of DNA and RNA
Genetic material of living organisms is either DNA or RNA.
DNA – Deoxyribonucleic acid
RNA – Ribonucleic acid
Genes are lengths of DNA that code for particular proteins.
Slide 3
AS Biology. Gnetic control of protein structure and function
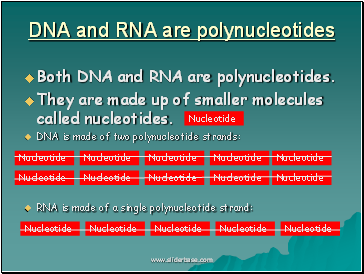
DNA and RNA are polynucleotides
Both DNA and RNA are polynucleotides.
They are made up of smaller molecules called nucleotides.
DNA is made of two polynucleotide strands:
RNA is made of a single polynucleotide strand:
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotide
Slide 4
AS Biology. Gnetic control of protein structure and function
Structure of a nucleotide
A nucleotide is made of 3 components:
A Pentose sugar
This is a 5 carbon sugar
The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose.
The sugar in RNA is ribose.
Slide 5
AS Biology.
Gnetic control of protein structure and function
Structure of a nucleotide
A Phosphate group
Phosphate groups are important because they link the sugar on one nucleotide onto the phosphate of the next nucleotide to make a polynucleotide.
Slide 6
AS Biology. Gnetic control of protein structure and function
Structure of a nucleotide
A Nitogenous base
In DNA the four bases are:
Thymine
Adenine
Cytosine
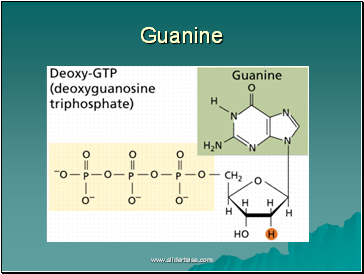
Guanine
In RNA the four bases are:
Uracil
Adenine
Cytosine
Guanine
Slide 7
AS Biology. Gnetic control of protein structure and function
Nitrogenous bases – Two types
Pyramidines
Thymine - T
Cytosine - C
Uracil - U
Purines
Adenine - A
Guanine - G
Slide 8
AS Biology. Gnetic control of protein structure and function
Adenine
Slide 9
AS Biology. Gnetic control of protein structure and function
Guanine
Contents
- AS Biology.
- Structure of a nucleotide
- Nitrogenous bases – Two types
- Adenine
- Guanine
- Sugar phosphate bonds (backbone of DNA)
- X-ray diffraction photograph of the DNA double helix
- Base pairing
- Complementary base pairing
- Nature of the Genetic Material
- Replication of DNA and Chromosomes
- A replicating Drosophila chromosome
Last added presentations
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Health Physics
- Friction
- Gravitation
- Newton's Laws
- Buoyancy
- Radiation