Cell Membrane + Tissues & Organs DefinitionsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Cells and Organelles;
The Cell Membrane
Book Reference: p.16-p.19
Slide 2
Do all membranes have the same basic structure?
Both the cell surface membrane and the membranes surrounding certain organelles have the same basic structure. Much of the membrane is made up of a 'sea' of phospholipids with protein molecules 'floating' in between the phospholipids.
Slide 3
Where are proteins located within the membrane?
What is an intrinsic protein?
What is an extrinsic protein?
Why is it called the fluid mosaic model?
Slide 4
INTRINSIC 1:
Channel Proteins
Allow movement of substances, such as glucose, across the membrane
NO ATP REQUIRED
Slide 5
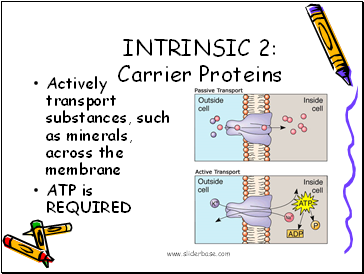
Actively transport substances, such as minerals, across the membrane
ATP is REQUIRED
INTRINSIC 2:
Carrier Proteins
Slide 6
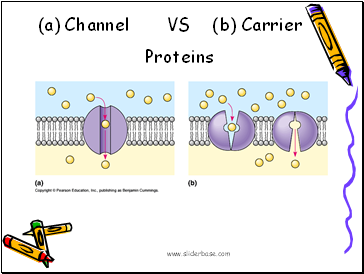
(a) Channel VS (b) Carrier
Proteins
Slide 7
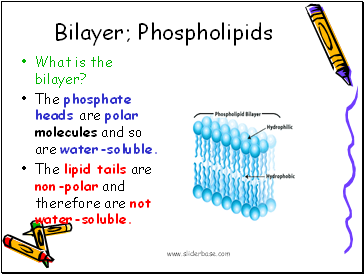
Bilayer; Phospholipids
What is the bilayer?
The phosphate heads are polar molecules and so are water-soluble.
The lipid tails are non-polar and therefore are not water-soluble.
Slide 8
Why do phospholipids have both a hydrophilic and a hydrophobic part?
The phosphate heads are polar. Are they water-soluble?
The lipid tails are non-polar. Are they water-soluble?
Slide 9
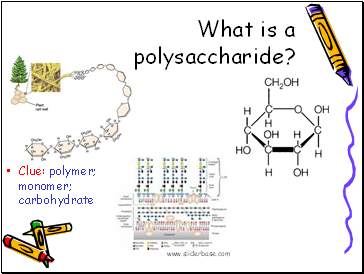
What is a polysaccharide?
Clue: polymer; monomer; carbohydrate
Slide 10
Slide 11
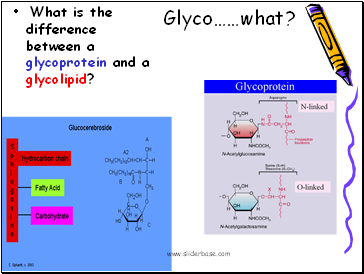
Glyco……what?
What is the difference between a glycoprotein and a glycolipid?
Slide 12
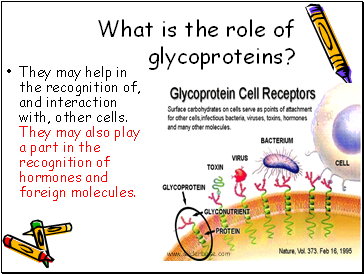
What is the role of glycoproteins?
They may help in the recognition of, and interaction with, other cells. They may also play a part in the recognition of hormones and foreign molecules.
Slide 13
What is the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
Cholesterol is also present in the membrane. It maintains the fluidity and increases the stability of the membrane. Without cholesterol the membrane would easily split apart
1 2
Contents
- The Cell Membrane
- Channel Proteins
- Carrier Proteins
- Bilayer; Phospholipids
- Cell membrane: Functions
- Cells and Organelles; Tissues
- What is a Tissue?
Last added presentations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Gravitation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Newton's Laws
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations