Immune SystemPage
1
1
Slide 1
The Immune System
Slide 2
Vocabulary
Infection
Invasion by foreign organisms such as viruses, fungi, bacteria
Immunity
Long term resistance to re-infection by organisms previously encountered
Antigens
Any material that elicits an immune response
Slide 3
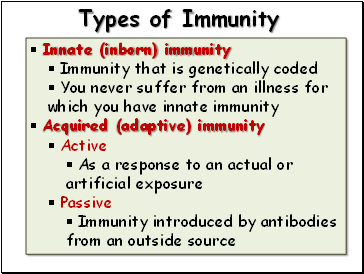
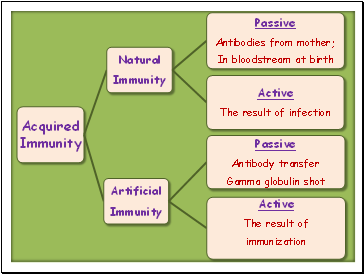
Types of Immunity
Innate (inborn) immunity
Immunity that is genetically coded
You never suffer from an illness for which you have innate immunity
Acquired (adaptive) immunity
Active
As a response to an actual or artificial exposure
Passive
Immunity introduced by antibodies from an outside source
Slide 4
Slide 5
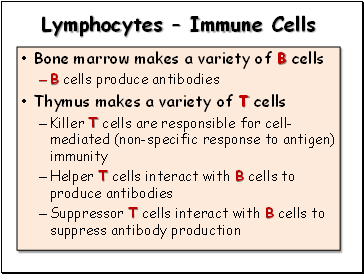
Lymphocytes – Immune Cells
Bone marrow makes a variety of B cells
B cells produce antibodies
Thymus makes a variety of T cells
Killer T cells are responsible for cell-mediated (non-specific response to antigen) immunity
Helper T cells interact with B cells to produce antibodies
Suppressor T cells interact with B cells to suppress antibody production
Slide 6
Antibodies
Highly specific proteins that bind to “nonself” materials
Each B cell can make only one antibody, and all descendents will produce the same antibody
B Cells have antibodies on their surface identical to the one that they produce
Long lived B cells (Memory Cells) quickly produce large quantities of antibodies to prevent illness
Slide 7
Antibody Structure
Slide 8
Edward Jenner and Smallpox (1798)
Observation
Milk maids who got cowpox were resistant to cowpox
Experiment
Injected a boy with pus from cowpox sores on infected udders
Results
Boy was protected against smallpox
Vaccination, from vaca, Latin for cow
Slide 9
Slide 10
Small Pox
Vaccination led to world-wide eradication announced in 1979 by World Health Organization
Slide 11
Polio: Not Eradicated
Slide 12
Diptheria: Not Eradicated
1 2
Contents
- Vocabulary
- Types of Immunity
- Lymphocytes – Immune Cells
- Antibodies
- Edward Jenner and Smallpox (1798)
- Small Pox
- Polio: Not Eradicated
- Diptheria: Not Eradicated
- Immunization Schedule
- Incubation Periods
- Autoimmune Diseases
Last added presentations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Motion
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation