Emergence of the animal kingdomPage
1
1
Slide 1
Emergence of the Animal Kingdom
Or “Rise of the Chordates”
Phylum Chordata
Leading to
Subphylum Vertebrata
Slide 2
Chordates include the following:
Fish
Reptiles
Amphibians
Birds
Mammals
Slide 3
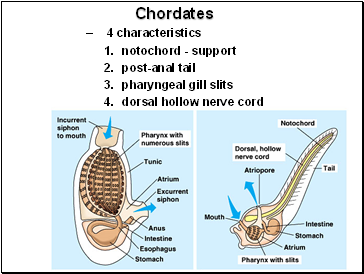
Chordates
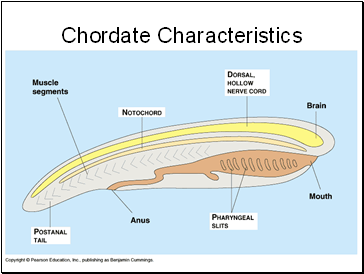
4 characteristics
notochord - support
post-anal tail
pharyngeal gill slits
dorsal hollow nerve cord
Slide 4
Chordate Characteristics
Slide 5
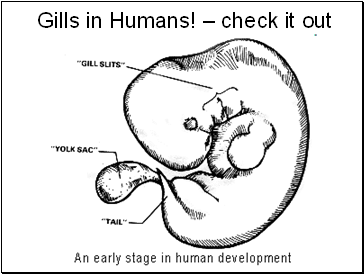
Gills in Humans! – check it out
Slide 6
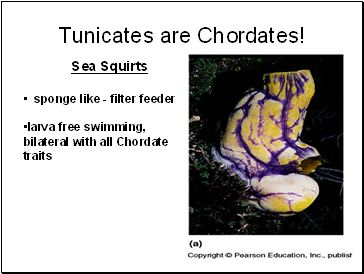
Tunicates are Chordates!
Sea Squirts
sponge like - filter feeder
larva free swimming, bilateral with all Chordate traits
Slide 7
Lancets (a primitive fish like organism) closely resembles the idealized chordate.
The notochord, dorsal nerve cord, numerous gill slits, and post-anal tail all persist in the adult
Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Slide 8
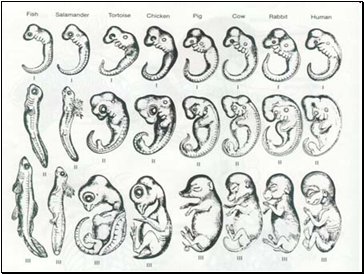
“Ontogency Recapituates Evolution” Evolution Playing out in Fetus… (all these Chordates (birds, mammals, reptiles, fish, have strikingly similar Embryonic Development)
Slide 9
Slide 10
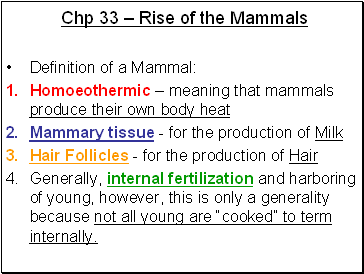
Chp 33 – Rise of the Mammals
Definition of a Mammal:
Homoeothermic – meaning that mammals produce their own body heat
Mammary tissue - for the production of Milk
Hair Follicles - for the production of Hair
Generally, internal fertilization and harboring of young, however, this is only a generality because not all young are “cooked” to term internally.
Slide 11
Monotremes – an Order of Class Mammalia
Monotremes
eg. The Platypus, which has a BILL, lays EGGS, but still has mammary glands and produces MILK for young. This suggests a relationship between REPTILES, BIRDS and mammals. Imagine that?
Slide 12
Marsupials
– eg. The Kangaroo, which is a non-placental mammal. Here, the development of the young is very complex, and a baby kangaroo is born very “uncooked”, and must crawl into the mother’s pouch and latch onto a nipple to receive milk to continue development. You might say, baby Kangaroos or “Joey’s” get a womb with a view
1 2
Contents
- Chordates include the following:
- Chordates
- Tunicates are Chordates!
- Chp 33 – Rise of the Mammals
- Monotremes – an Order of Class Mammalia
- Marsupials
- Placental Mammals
- Skeletal System
- Muscular System
- Advanced Circulatory System
- Respiratory System
- Nervous System is online and advanced!
Last added presentations
- Thermal Energy
- Friction
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions