ADH Diagram animatedPage
1
1
Slide 1
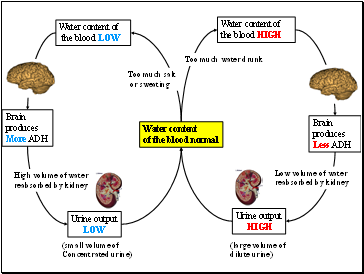
Water content
of the blood normal
Water content of the blood HIGH
Water content of
the blood LOW
Too much water drunk
Too much salt
or sweating
Brain produces
More ADH
Urine output
LOW
Brain produces
Less ADH
Urine output
HIGH
High volume of water
reabsorbed by kidney
Low volume of water
reabsorbed by kidney
(small volume of
Concentrated urine)
(large volume of
dilute urine)
Slide 2
Click on the screen icon below to run the tutorial
(then click the mouse button to make it play through)
Slide 3
All land animals need to conserve water.
This is because the external environment is usually drier than the internal environment of the animal’s body. Thus, water will tend to diffuse away from the body.
There is also a need to excrete waste products such as urea, which is dissolved in water. This creates a problem!
In mammals, the kidneys are responsible for both excretion of urea and osmoregulation (the control of body fluid concentration).
So, the kidney must balance the need to excrete with the need to conserve water, in other words it must produce a small volume of highly concentrated urine.
Slide 4
The operating unit of the kidney is called the nephron.
There are about 1 million nephrons in each of the 2 kidneys.
Each nephron comprises 5 segments:
Glomerulus
Proximal (first) convoluted tubule
Loop of Henle
Distal (second) convoluted tubule
Collecting duct
The Loop of Henle allows mammals to produce urine which is more concentrated than body fluids… .
Slide 5
Cortex
Medulla
The nephrons are packed into the kidney:
the glomeruli and convoluted tubules in the cortex,
the loops and collecting ducts extending into the medulla.
All the collecting ducts eventually join up to form the ureter,
emptying urine into the bladder and away!
Ureter
Slide 6
Cortex
Water leaves - ion concentration in filtrate increases
Filtrate reaches maximum concentration
Chloride ions out (sodium follows) -ion concentration in filtrate decreases
Medulla
Increasing concentration
Slide 7
Increasing concentration
To ureter
Collecting duct
Several nephrons empty into one collecting duct.
The collecting duct passes through the progressively more concentrated medulla, losing water by osmosis. This water is reabsorbed by the capillaries.
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Newton's laws of motion
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Buoyancy
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants