BuffersPage
1
1
Slide 1
Buffers and Acid/Base Titration
Slide 2
Reaction of Weak Bases with Water
The base reacts with water, producing its conjugate acid and hydroxide ion:
CH3NH2 + H2O CH3NH3+ + OH- Kb = 4.38 x 10-4
Slide 3
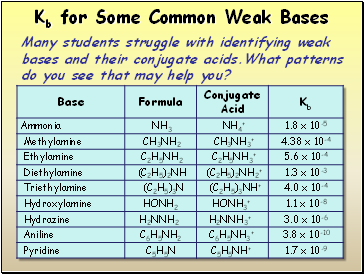
Kb for Some Common Weak Bases
Many students struggle with identifying weak bases and their conjugate acids.What patterns do you see that may help you?
Slide 4
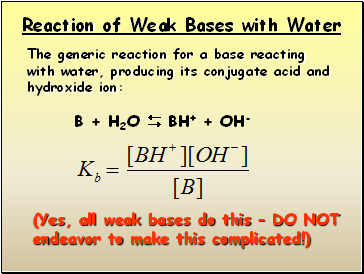
Reaction of Weak Bases with Water
The generic reaction for a base reacting with water, producing its conjugate acid and hydroxide ion:
B + H2O BH+ + OH-
(Yes, all weak bases do this – DO NOT
endeavor to make this complicated!)
Slide 5
Buffered Solutions
A solution that resists a change in pH when either hydroxide ions or protons are added.
Buffered solutions contain either:
A weak acid and its salt
A weak base and its salt
Slide 6
Acid/Salt Buffering Pairs
The salt will contain the anion of the acid, and the cation of a strong base (NaOH, KOH)
Slide 7
Base/Salt Buffering Pairs
The salt will contain the cation of the base, and the anion of a strong acid (HCl, HNO3)
Slide 8
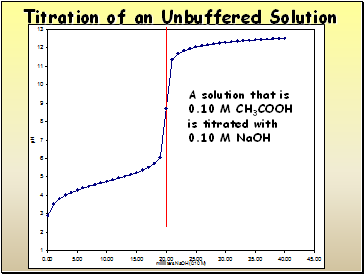
Titration of an Unbuffered Solution
A solution that is
0.10 M CH3COOH
is titrated with
0.10 M NaOH
Slide 9
Titration of a Buffered Solution
A solution that is
0.10 M CH3COOH and
0.10 M NaCH3COO is titrated with
0.10 M NaOH
Slide 10
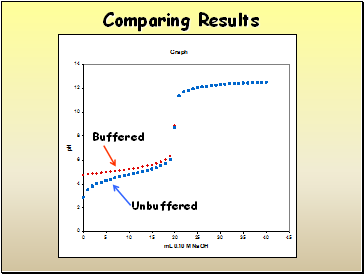
Comparing Results
Buffered
Unbuffered
Slide 11
Comparing Results
Unbuffered
Buffered
In what ways are the graphs different?
In what ways are the graphs similar?
Slide 12
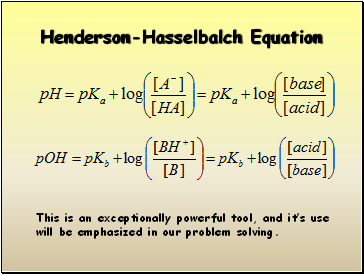
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
This is an exceptionally powerful tool, and it’s use will be emphasized in our problem solving.
Slide 13
Weak Acid/Strong Base Titration
1 2
Contents
- Reaction of Weak Bases with Water
- Kb for Some Common Weak Bases
- Reaction of Weak Bases with Water
- Buffered Solutions
- Acid/Salt Buffering Pairs
- Base/Salt Buffering Pairs
- Titration of an Unbuffered Solution
- Comparing Results
- Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- Weak Acid/Strong Base Titration
- Strong Acid/Strong Base Titration
- Selection of Indicators
- Indicator Transitions
Last added presentations
- Upcoming Classes
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Motion
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation