Basic Biochemistry - Carbohydrate, Protein and FatPage
1
1
Slide 1
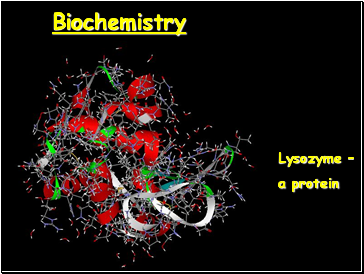
Biochemistry
Lysozyme –
a protein
Slide 2
Carbohydrates
There are two types of carbohydrates:
The simple sugars
Glucose, sucrose, fructose (and many others)
The complex carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates that are made of long chains of sugars
Starches, cellulose
Slide 3
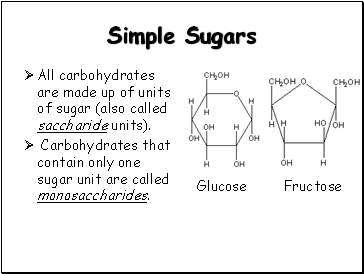
Simple Sugars
All carbohydrates are made up of units of sugar (also called saccharide units).
Carbohydrates that contain only one sugar unit are called monosaccharides.
Glucose
Fructose
Slide 4
Simple Sugars
Disaccharides have two sugar units bonded together.
For example, common table sugar is sucrose (below), a disaccharide that consists of a glucose unit bonded to a fructose unit.
Slide 5
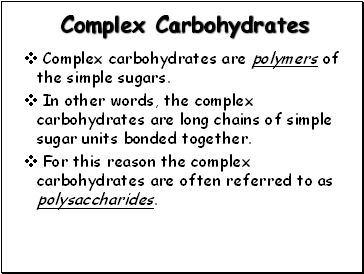
Complex Carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates are polymers of the simple sugars.
In other words, the complex carbohydrates are long chains of simple sugar units bonded together.
For this reason the complex carbohydrates are often referred to as polysaccharides.
Slide 6
Complex Carbohydrates
Starch (below) is a polymer of the monosaccharide glucose (n is the number of repeating glucose units and ranges in the 1,000's).
Starches and cellulose are complex carbohydrates used by plants for energy storage and structural integrity.
Slide 7
Complex Carbohydrates
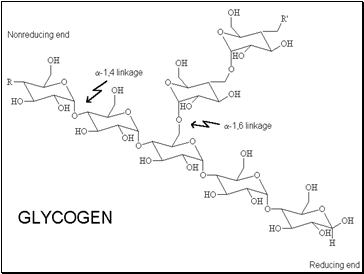
Glycogen, another polymer of glucose, is the polysaccharide used by animals to store energy.
Both starch and glycogen are polymers of glucose.
Starch is a long, straight chain of glucose units, whereas glycogen is a branched chain of glucose units.
Slide 8
Structure of Glycogen
Slide 9
Proteins
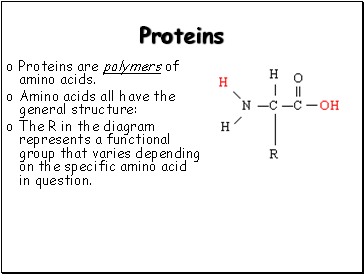
Proteins are polymers of amino acids.
Amino acids all have the general structure:
The R in the diagram represents a functional group that varies depending on the specific amino acid in question.
Slide 10
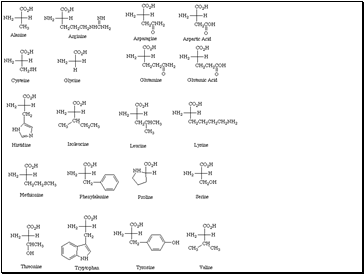
Twenty amino acids in human metabolism
Slide 11
Proteins
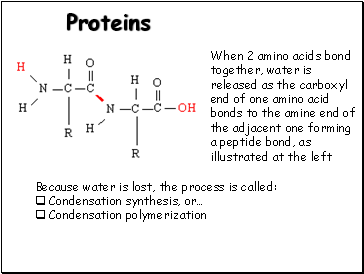
When 2 amino acids bond together, water is released as the carboxyl end of one amino acid bonds to the amine end of the adjacent one forming a peptide bond, as illustrated at the left.
1 2
Contents
- Biochemistry
- Carbohydrates
- Simple Sugars
- Complex Carbohydrates
- Structure of Glycogen
- Proteins
- Insulin
- Fats
- Saturated Fats
- Mono-Unsaturated Fats
- Poly-Unsaturated Fats
Last added presentations
- Newton's laws of motion
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Thermal Energy
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Newton's Laws