AzocompoundsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Azo Compounds
Slide 2
What are azo compounds?
Contain the -N=N- group.
Where R and R’ are arene groups more stable than alkyl groups.
Azo group is stabilised by becoming part of extended delocalised system.
Result of a coupling reaction between a diazonium salt and a coupling agent.
R-N=N-R'
Azo group
Slide 3
Diazonium salts
Only stable salts are aromatic - not particularly stable.
Lose -N+N as N2(g)
Electron rich benzene ring stabilises the -N+N group but decomposition occurs above about 5oC.
Add cold soln. sodium nitrite (NaNO2) to arylamine soln. In dilute acid below 5oC.
Diazotisation.
Prepare fresh and use immediately.
Slide 4
How the salt is made.
Acid reacts with sodium nitrite to form unstable nitrous acid.
NaNO2 (aq) + HCl (aq) HNO2 (aq) + NaCl (aq)
Nitrous acid reacts with the arylamine.
phenylamine
benzenediazonium ion
Slide 5
Diazo coupling reactions
A diazonium salt reacts with another compound containing a benzene ring called a coupling agent.
Diazonium salt acts as an electrophile - reacts with benzene ring of coupling agent.
Coloured precipitate of azo compound immediately forms.
Important use as dyes.
Slide 6
Coupling with phenols
Benzenediazonium salt and alkaline phenol gives a yellow orange azo compound
Benzenediazonium salt and alkaline naphthalen-2-ol gives a red azo compound.
Slide 7
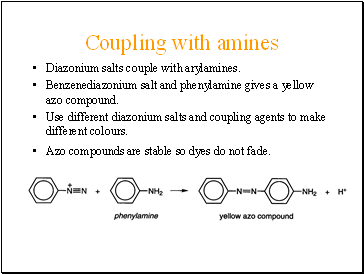
Coupling with amines
Diazonium salts couple with arylamines.
Benzenediazonium salt and phenylamine gives a yellow azo compound.
Use different diazonium salts and coupling agents to make different colours.
Azo compounds are stable so dyes do not fade.
Contents
- Azo Compounds
- What are azo compounds?
- Diazonium salts
- How the salt is made.
- Diazo coupling reactions
- Coupling with phenols
- Coupling with amines
Last added presentations
- Radiation
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Health Physics
- Gravitation
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation