Addition ReactionsPage
1
1
Slide 1
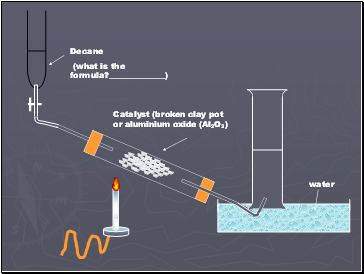
Catalyst (broken clay pot or aluminium oxide (Al2O3)
Decane
(what is the formula? )
water
Slide 2
Decane
(what is the formula? )
What is the Structural formula - Draw in your jotter)
Slide 3
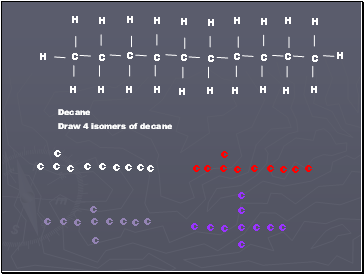
Decane
Draw 4 isomers of decane
Slide 4
When we “crack” DECANE what are the possible products formed?
How do you prove you have formed these products?
H
Slide 5
Annapurna
Slide 6
Pentene
CH3CH2CH2CH=CH2
Alkenes
Can be
Hydrocarbons
Saturated
(Single Bonds)
Can be
Unsaturated
(Double Bond)
Ethene
CH2=CH2
Alkanes
Cycloalkanes
Slide 7
Slide 8
Saturated or Unsaturated?
CH2CHCH3
Saturated
Saturated
Saturated
Unsaturated
Unsaturated
Slide 9
Bromine Water
Br
Br
Double Bonds
Undergo
Addition Reactions
In Addition Reactions
The double bond
Breaks and bromine atoms
are added to both sides
of the double bond
Slide 10
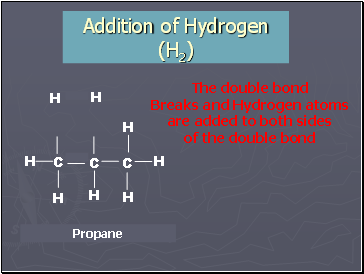
Addition of Hydrogen (H2)
H
H
The double bond
Breaks and Hydrogen atoms
are added to both sides
of the double bond
Propene + Hydrogen
Propane
Slide 11
Alkenes into Alkanes
Hexene + Hydrogen
C6H12
H2
+
Hexane
C6H14
Now write this reactions using the Structural Formulae
1.
Slide 12
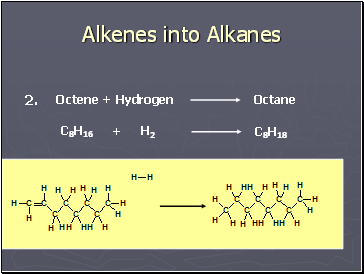
Alkenes into Alkanes
Octene + Hydrogen
Octane
C8H16
H2
+
C8H18
2.
Slide 13
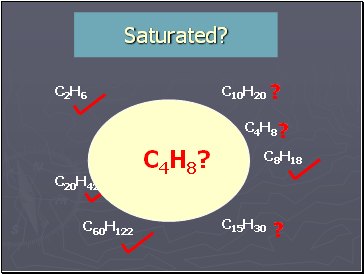
Saturated?
C2H6
C4H10
C20H42
C10H20
C15H30
C8H18
C7H14
C60H122
C11H22
?
?
?
?
C4H8
?
Slide 14
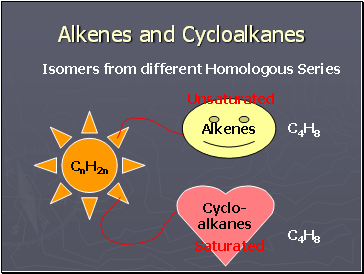
Alkenes and Cycloalkanes
Isomers from different Homologous Series
1 2
Contents
- Annapurna
- Saturated or Unsaturated?
- Bromine Water
- Addition of Hydrogen (H2)
- Alkenes into Alkanes
- Saturated?
- Alkenes and Cycloalkanes
Last added presentations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Buoyancy
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Solar Thermal Energy