The UniversePage
1
1
Slide 1
The Universe
Slide 2
Cosmology
Cosmology is the study of the nature of the universe, how the universe began and how it will end, if it does
There is religious cosmology, and scientific cosmology
“Creation myths” from traditional cultures are a form of cosmology
Scientific cosmology is part of astronomy and physics
Slide 3
Newton’s Static Universe
Here’s what Isaac Newton thought:
The universe is static (unchanging) and made of an infinite number of stars that are scattered randomly throughout an infinite space
The universe is infinitely old and will exist forever without any major changes
This is also called the “steady state” model
Is this true?
Slide 4
Edwin Hubble’s Discovery
Hubble noticed that the further away the galaxy, the greater the redshift of its light
Redshift is the Doppler Effect for light waves from objects moving away from the observer
Slide 5
What does this redshift mean?
The greater a galaxy’s distance from the observer, the greater its speed moving away from the observer, based on its greater redshift
So, galaxies are getting farther apart as time moves forward, therefore the universe is expanding (getting bigger)
Slide 6
How old is the universe?
Hubble showed that the universe has been expanding for billions of years
The universe was denser in the past
If we “run the film backwards” to when the universe was a single point in space and infinitely dense, that happened about 13.7 billion (13,700,000,000) years ago
This was the “Big Bang”
Slide 7
The Big Bang
Most scientists believe the universe as we know it began with the big bang
This created space and time as we know them, so in a real sense, there was no “before the big bang,” and the big bang didn’t happen “in space”
Slide 8
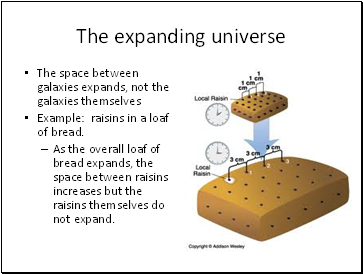
The expanding universe
The space between galaxies expands, not the galaxies themselves
Example: raisins in a loaf of bread.
As the overall loaf of bread expands, the space between raisins increases but the raisins themselves do not expand.
Slide 9
Dark energy and dark matter
1 2
Contents
- The Universe
- Cosmology
- Newton’s Static Universe
- Edwin Hubble’s Discovery
- What does this redshift mean?
- How old is the universe?
- The Big Bang
- The expanding universe
- Dark energy and dark matter
- How will the universe end?
- The anthropic principle
- We still don’t know:
Last added presentations
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Buoyancy
- Space Radiation
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Friction
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation