Significant FiguresPage
1
1
Slide 1
Uncertainty and Significant Figures
Cartoon courtesy of Lab-initio.com
Slide 2
Uncertainty in Measurement
A digit that must be estimated is called uncertain. A measurement always has some degree of uncertainty.
Slide 3
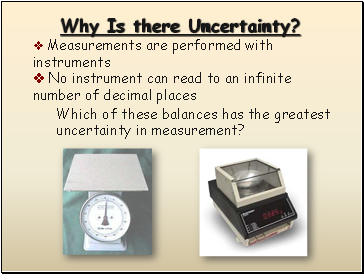
Why Is there Uncertainty?
Measurements are performed with instruments
No instrument can read to an infinite number of decimal places
Which of these balances has the greatest uncertainty in measurement?
Slide 4
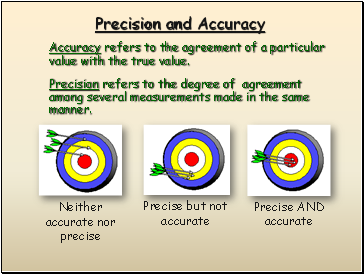
Precision and Accuracy
Accuracy refers to the agreement of a particular value with the true value.
Precision refers to the degree of agreement among several measurements made in the same manner.
Neither accurate nor precise
Precise but not accurate
Precise AND accurate
Slide 5
Types of Error
Random Error (Indeterminate Error) - measurement has an equal probability of being high or low.
Systematic Error (Determinate Error) - Occurs in the same direction each time (high or low), often resulting from poor technique or incorrect calibration.
Slide 6
Rules for Counting Significant Figures - Details
Nonzero integers always count as significant figures.
3456 has
4 significant figures
Slide 7
Rules for Counting Significant Figures - Details
Zeros
- Leading zeros do not count as
significant figures.
0.0486 has
3 significant figures
Slide 8
Rules for Counting Significant Figures - Details
Zeros
- Captive zeros always count as
significant figures.
16.07 has
4 significant figures
Slide 9
Rules for Counting Significant Figures - Details
Zeros
Trailing zeros are significant only if the number contains a decimal point.
9.300 has
4 significant figures
Slide 10
Rules for Counting Significant Figures - Details
Exact numbers have an infinite number of significant figures.
1 inch = 2.54 cm, exactly
Slide 11
Sig Fig Practice #1
1 2
Contents
- Uncertainty and Significant Figures
- Uncertainty in Measurement
- Why Is there Uncertainty?
- Precision and Accuracy
- Types of Error
- Rules for Counting Significant Figures - Details
Last added presentations
- Madame Marie Curie
- Motion
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Radiation
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy