Properties of Acids BasesPage
1
1
Slide 1
ACIDS AND BASES
Slide 2
CA Standards
Slide 3
Properties of Acids
Acids are proton (hydrogen ion, H+) donors
Acids have a pH lower than 7
Acids taste sour
Acids effect indicators
Blue litmus turns red
Methyl orange turns red
Acids react with active metals, producing H2
Acids react with carbonates
Acids neutralize bases
Slide 4
Acids are Proton (H+ ion) Donors
Strong acids are assumed to be 100% ionized in solution (good H+ donors).
Weak acids are usually less than 5% ionized in solution (poor H+ donors).
HCl
H2SO4
HNO3
H3PO4
HC2H3O2
Organic acids
Slide 5
Acids Have a pH less than 7
Slide 6
Acids Taste Sour
Citric acid in citrus fruit
Malic acid in sour apples
Lactic acid in sour milk and sore muscles
Butyric acid in rancid butter
Organic acids are weak acids. Some are used as flavoring agents in food.
Slide 7
Organic Acids
Organic acids all contain the “carboxyl” group, sometimes several of them.
The carboxyl group is a poor proton donor, so ALL organic acids are weak acids.
Slide 8
Acids Effect Indicators
Blue litmus paper turns red in contact with an acid.
Methyl orange turns red with addition of an acid
Slide 9
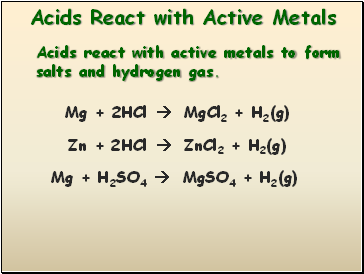
Acids React with Active Metals
Acids react with active metals to form salts and hydrogen gas.
Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2(g)
Zn + 2HCl ZnCl2 + H2(g)
Mg + H2SO4 MgSO4 + H2(g)
Slide 10
Acids React with Carbonates
2HC2H3O2 + Na2CO3
2 NaC2H3O2 + H2O + CO2
Slide 11
Effects of Acid Rain on Marble (calcium carbonate)
George Washington:
BEFORE
George Washington:
AFTER
Slide 12
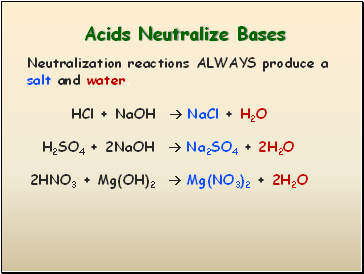
Acids Neutralize Bases
HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O
Neutralization reactions ALWAYS produce a salt and water.
1 2
Contents
- Properties of Acids
- Acids are Proton (H+ ion) Donors
- Acids Taste Sour
- Organic Acids
- Acids Effect Indicators
- Acids React with Active Metals
- Acids React with Carbonates
- Acids Neutralize Bases
- Properties of Bases
- Bases are Proton (H+ ion) Acceptors
- Bases Effect Indicators
- Bases Neutralize Acids
Last added presentations
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Waves & Sound
- Upcoming Classes
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms