Alpha ParticlesPage
1
1
Slide 1
Alpha Particles
Alpha Particles: 2 neutrons and 2 protons
They travel short distances, have large mass
Only a hazard when inhaled
Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation:
Slide 2
Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation: Beta Particles
Beta Particles: Electrons or positrons having small mass and variable energy. Electrons form when a neutron transforms into a proton and an electron or:
Slide 3
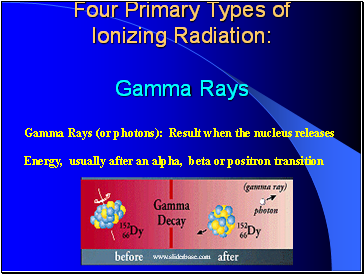
Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation: Gamma Rays
Gamma Rays (or photons): Result when the nucleus releases
Energy, usually after an alpha, beta or positron transition
Slide 4
Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation: X-Rays
X-Rays: Occur whenever an inner shell orbital electron is removed
and rearrangement of the atomic electrons results with the release of
the elements characteristic X-Ray energy
Slide 5
Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation: Neutrons
Neutrons: Have the same mass as protons but are uncharged
They behave like bowling balls
Slide 6
Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation
Alpha particles
Beta particles
Gamma rays (or photons)
X-Rays (or photons)
Neutrons
Slide 7
Radiation fundamentals atomic and nuclear structure
Bureau of Radiation Control
Slide 8
Radioactivity: Elements & Atoms
Atoms are composed of smaller particles referred to as:
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
Slide 9
Ionization
•Ionizing radiation is produced by unstable atoms. Unstable atoms differ from stable atoms because they have an excess of energy or mass or both.
•Unstable atoms are said to be radioactive. In order to reach stability, these atoms give off, or emit, the excess energy or mass. These emissions are called radiation.
•
Slide 10
Types or Products of Ionizing Radiation
or X-ray
neutron
Slide 11
Radioactive Atom
X-ray
gamma ray
Contents
Last added presentations
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Radiation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy