Community EcologyPage
1
1
Slide 1
A Sense of Community
A biological community is an assemblage of populations of various species living close enough for potential interaction. All life / all populations in an area.
Ecologists call relationships between species in a community interspecific interactions.
Interspecific interactions can affect the survival and reproduction of each species. Effects can be positive (+), negative (–), or no effect (0).
Examples: competition, predation, herbivory, and symbiosis (parasitism, mutualism, commensalism).
Slide 2
Competition
Interspecific competition (–/– interaction) occurs when different species compete for a resource in short supply.
Strong competition can lead to competitive exclusion, local elimination of a competing species.
The competitive exclusion principle states that two species competing for the same limiting resources cannot coexist in the same place = 1 species per niche.
Slide 3
Ecological Niches
The total of a species’ use of biotic and abiotic resources is called the species’ ecological niche.
An ecological niche can also be thought of as an organism’s ecological role.
Ecologically similar species can coexist in a community if there are one or more significant differences in their niches.
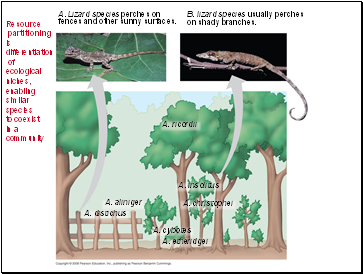
Resource partitioning is differentiation of ecological niches; enables similar species to coexist in a community.
Slide 4
Resource partitioning is differentiation of ecological niches, enabling similar species to coexist in a community
A. ricordii
B. lizard species usually perches
on shady branches.
A. Lizard species perches on
fences and other sunny surfaces.
A. aliniger
A. distichus
A. insolitus
A. christophei
A. cybotes
A. etheridgei
Slide 5
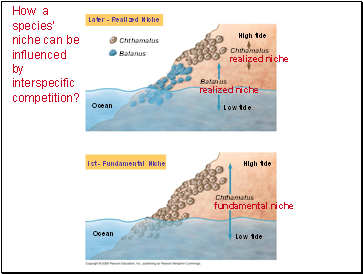
As a result of interspecific competition, a species’ fundamental niche may differ from its realized niche --> the niche it occupys after resource partitioning.
Interspecific => Competition Between Species: Can Lead to Resource Partitioning
Slide 6
How a species’ niche can be influenced by interspecific competition?
Ocean
Chthamalus
Balanus
Later - Realized Niche
Ist - Fundamental Niche
High tide
Low tide
Chthamalus
realized niche
Balanus
realized niche
High tide
Chthamalus
fundamental niche
Low tide
Ocean
Slide 7
Contents
- A Sense of Community
- Predation
- Dominant and keystone species exert strong controls on community structure
- Species Diversity
- Bottom-Up and Top-Down Controls
- Disturbance influences species diversity and composition
- Characterizing Disturbance
- Ecological Succession
- Human Disturbance
- Biogeographic factors affect community biodiversity
- Area Effects
- Island Equilibrium Model
- Community ecology is useful for understanding pathogen life cycles and controlling human disease
- Community Ecology and Zoonotic Diseases
Last added presentations
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Upcoming Classes
- Sound
- Newton’s third law of motion