Membrane Structure and FunctionPage
1
1
Slide 1
Life at the Edge
The plasma membrane is the boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings
The plasma membrane exhibits selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than others
Slide 2
Fig. 7-1
Slide 3
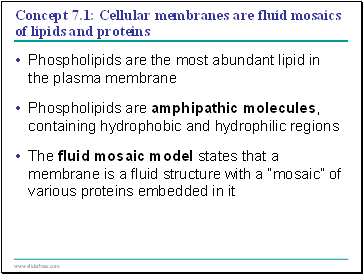
Concept 7.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins
Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, containing hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
The fluid mosaic model states that a membrane is a fluid structure with a “mosaic” of various proteins embedded in it
Slide 4
Membrane Models: Scientific Inquiry
Membranes have been chemically analyzed and found to be made of proteins and lipids
Scientists studying the plasma membrane reasoned that it must be a phospholipid bilayer
Slide 5
Fig. 7-2
Hydrophilic
head
WATER
Hydrophobic
tail
WATER
Slide 6
In 1935, Hugh Davson and James Danielli proposed a sandwich model in which the phospholipid bilayer lies between two layers of globular proteins
Later studies found problems with this model, particularly the placement of membrane proteins, which have hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
In 1972, J. Singer and G. Nicolson proposed that the membrane is a mosaic of proteins dispersed within the bilayer, with only the hydrophilic regions exposed to water
Slide 7
Fig. 7-3
Phospholipid
bilayer
Hydrophobic regions
of protein
Hydrophilic
regions of protein
Slide 8
Freeze-fracture studies of the plasma membrane supported the fluid mosaic model
Freeze-fracture is a specialized preparation technique that splits a membrane along the middle of the phospholipid bilayer
Slide 9
Fig. 7-4
TECHNIQUE
Extracellular
layer
Knife
Proteins
Inside of extracellular layer
RESULTS
Inside of cytoplasmic layer
Cytoplasmic layer
Plasma membrane
Slide 10
The Fluidity of Membranes
Phospholipids in the plasma membrane can move within the bilayer
Contents
- Life at the Edge
- Membrane Models: Scientific Inquiry
- The Fluidity of Membranes
- Membrane Proteins and Their Functions
- The Role of Membrane Carbohydrates in Cell-Cell Recognition
- Synthesis and Sidedness of Membranes
- The Permeability of the Lipid Bilayer
- Transport Proteins
- Effects of Osmosis on Water Balance
- Water Balance of Cells with Walls
- Facilitated Diffusion: Passive Transport Aided by Proteins
- The Need for Energy in Active Transport
- How Ion Pumps Maintain Membrane Potential
- Cotransport: Coupled Transport by a Membrane Protein
- Exocytosis
- Endocytosis
Last added presentations
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Thermal Energy
- Sound
- Mechanics Lecture
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation