Hormones and the Endocrine SystemPage
1
1
Slide 1
The Body’s Long-Distance Regulators
Animal hormones are chemical signals that are secreted into the circulatory system and communicate regulatory messages within the body.
Hormones reach all parts of the body, but only target cells are equipped to respond.
Insect metamorphosis is regulated by hormones.
Slide 2
Two systems coordinate communication throughout the body: the endocrine system and the nervous system.
The endocrine system secretes hormones that coordinate slower but longer-acting responses including reproduction, development, energy metabolism, growth, and behavior.
The nervous system conveys high-speed electrical signals along specialized cells called neurons; these signals regulate other cells.
Slide 3
What role do hormones play in transforming a caterpillar into a butterfly?
Slide 4
Hormones and other signaling molecules bind to target receptors, triggering specific response pathways
Chemical signals bind to receptor proteins on target cells.
Only target cells respond to the signal.
Slide 5
Types of Secreted Signaling Molecules
Secreted chemical signals include
Hormones
Local regulators
Neurotransmitters
Neurohormones
Pheromones
Slide 6
Hormones
Endocrine signals (hormones) are secreted into extracellular fluids and travel via the bloodstream.
Endocrine glands are ductless and secrete hormones directly into surrounding fluid.
Hormones mediate responses to environmental stimuli and regulate growth, development, and reproduction.
Exocrine glands have ducts and secrete substances onto body surfaces or into body cavities (for example, tear ducts).
Slide 7
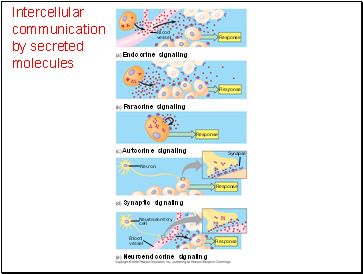
Intercellular communication by secreted molecules
Blood
vessel
Response
Response
Response
Response
(a) Endocrine signaling
(b) Paracrine signaling
(c) Autocrine signaling
(d) Synaptic signaling
Neuron
Neurosecretory
cell
(e) Neuroendocrine signaling
Blood
vessel
Synapse
Response
Slide 8
Local Regulators = Short Distance Chemical Signals
Local regulators are chemical signals that travel over short distances by diffusion.
Local regulators help regulate blood pressure, nervous system function, and reproduction.
Contents
- The Body’s Long-Distance Regulators
- Types of Secreted Signaling Molecules
- Local Regulators = Short Distance Chemical Signals
- Neurotransmitters and Neurohormones
- Pheromones
- Chemical Classes of Hormones
- Cellular Response Pathways
- Pathway for Water-Soluble Hormones
- Pathway for Lipid-Soluble Hormones
- Multiple Effects of Hormones
- Signaling by Local Regulators
- Simple Hormone Pathways
- Insulin and Glucagon: Control of Blood Glucose
- Target Tissues for Insulin and Glucagon
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Posterior Pituitary Hormones
- Anterior Pituitary Hormones
- Hormone Cascade Pathways
- Tropic Hormones
- Nontropic Hormones - target nonendocrine tissues.
- Growth Hormone
- Thyroid Hormone: Control of Metabolism and Development
- Parathyroid Hormone and Vitamin D: Control of Blood Calcium
- Adrenal Hormones: Response to Stress
- Catecholamines from the Adrenal Medulla
- Steroid Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex
- Gonadal Sex Hormones
- Pineal Gland - Melatonin and Biorhyths
Last added presentations
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Sound
- Friction
- Gravitation
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation