Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical EnergyPage
1
1
Slide 1
Life Is Work
Living cells require energy from outside sources
Some animals, such as the giant panda, obtain energy by eating plants, and some animals feed on other organisms that eat plants
Slide 2
Fig. 9-1
Slide 3
Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat
Photosynthesis generates O2 and organic molecules, which are used in cellular respiration
Cells use chemical energy stored in organic molecules to regenerate ATP, which powers work
Slide 4
Fig. 9-2
Light
energy
ECOSYSTEM
Photosynthesis
in chloroplasts
CO2 + H2O
Cellular respiration
in mitochondria
Organic
molecules
+ O2
ATP powers most cellular work
Heat
energy
ATP
Slide 5
Concept 9.1: Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels
Several processes are central to cellular respiration and related pathways
Slide 6
Catabolic Pathways and Production of ATP
The breakdown of organic molecules is exergonic
Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2
Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP
Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2
Slide 7
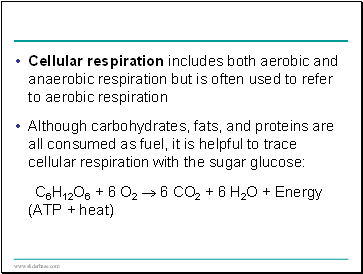
Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration
Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose:
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat)
Slide 8
Redox Reactions: Oxidation and Reduction
The transfer of electrons during chemical reactions releases energy stored in organic molecules
This released energy is ultimately used to synthesize ATP
Slide 9
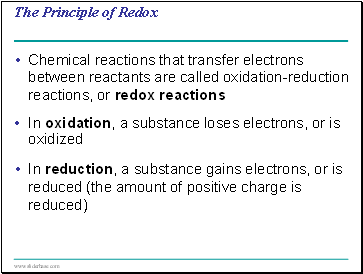
The Principle of Redox
Chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants are called oxidation-reduction reactions, or redox reactions
In oxidation, a substance loses electrons, or is oxidized
In reduction, a substance gains electrons, or is reduced (the amount of positive charge is reduced)
Contents
- Life Is Work
- Catabolic Pathways and Production of ATP
- Redox Reactions: Oxidation and Reduction
- The Principle of Redox
- The Stages of Cellular Respiration: A Preview
- The Pathway of Electron Transport
- Chemiosmosis: The Energy-Coupling Mechanism
- An Accounting of ATP Production by Cellular Respiration
- Types of Fermentation
- Fermentation and Aerobic Respiration Compared
- The Evolutionary Significance of Glycolysis
- The Versatility of Catabolism
- Biosynthesis (Anabolic Pathways)
- Regulation of Cellular Respiration via Feedback Mechanisms
Last added presentations
- Newton's Laws
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Madame Marie Curie
- Upcoming Classes
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations