Metallic BondingPage
1
1
Slide 1
Metallic Bonding
Strong forces of attraction are responsible for the high melting point of most metals.
Slide 2
CA Standards
Students know atoms combine to form molecules by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchanging electrons to form ionic bonds.
Slide 3
Metallic Bonding
The chemical bonding that results from the attraction between metal cations and the surrounding sea of electrons
Vacant p and d orbitals in metal's outer energy levels overlap, and allow outer electrons to move freely throughout the metal
Valence electrons do not belong to any one atom
Slide 4
Packing in Metals
Model: Packing uniform, hard spheres to best use available space. This is called closest packing. Each atom has 12 nearest neighbors.
Slide 5
Metal Alloys
Substitutional Alloy: some metal atoms replaced by others of similar size.
Slide 6
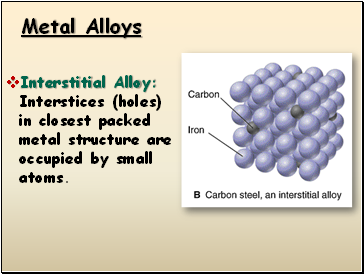
Metal Alloys
Interstitial Alloy: Interstices (holes) in closest packed metal structure are occupied by small atoms.
Slide 7
Properties of Metals
Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity
Metals are malleable
Metals are ductile
Metals have high tensile strength
Metals have luster
Contents
Last added presentations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Buoyancy
- Newton's Laws
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Space Radiation
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms