Strengths of Acids and Bases Making DilutionsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Chapter 9 Acids and Bases
Strengths of Acids and Bases
Making Dilutions
Slide 2
Strengths of Acids and Bases
Strong acids completely ionize (100%) in aqueous solutions
HCl + H2O H3O+ + Cl- (100 % ions)
Strong bases completely (100%) dissociate into ions in aqueous solutions.
NaOH Na+ (aq) + OH-(aq)
(100 % ions)
Slide 3
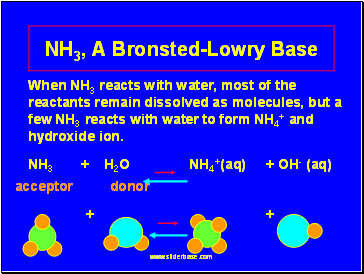
NH3, A Bronsted-Lowry Base
When NH3 reacts with water, most of the reactants remain dissolved as molecules, but a few NH3 reacts with water to form NH4+ and hydroxide ion.
NH3 + H2O NH4+(aq) + OH- (aq)
acceptor donor
+ +
Slide 4
Strong and Weak Acids and Bases
Strong acids
HCl, HNO3 , H2SO4
Most other acids are weak.
Strong bases
NaOH, KOH, and Ca(OH)2
Most other bases are weak.
Slide 5
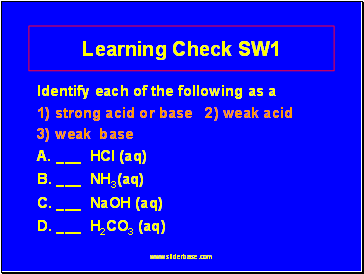
Learning Check SW1
Identify each of the following as a
1) strong acid or base 2) weak acid
3) weak base
A. _ HCl (aq)
B. _ NH3(aq)
C. _ NaOH (aq)
D. _ H2CO3 (aq)
Slide 6
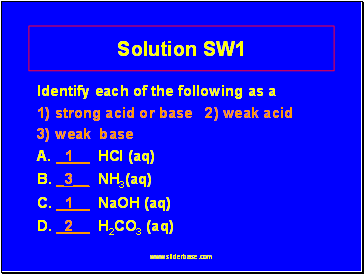
Solution SW1
Identify each of the following as a
1) strong acid or base 2) weak acid
3) weak base
A. _1 HCl (aq)
B. _3 NH3(aq)
C. _1 NaOH (aq)
D. _2 H2CO3 (aq)
Slide 7
Antacids
Used to neutralize stomach acid (HCl)
Many contain one or more weak bases
Alka-Seltzer: NaHCO3, citric acid, and aspirin
Di-gel: CaCO3 and Mg(OH)2
Gelusil: Al(OH)3 and Mg(OH)2
Maalox: Al(OH)3 and Mg(OH)2
Mylanta: Al(OH)3 and Mg(OH)2
Slide 8
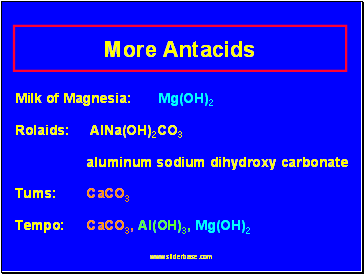
More Antacids
Milk of Magnesia: Mg(OH)2
Rolaids: AlNa(OH)2CO3
aluminum sodium dihydroxy carbonate
Tums: CaCO3
Tempo: CaCO3, Al(OH)3, Mg(OH)2
Slide 9
Dilutions
Add water
Volume increases.
New concentration is less than initial
Slide 10
Concentration of A Diluted Solution
A 25 mL sample of a 6.0 M KOH is diluted by adding 75 mL of water. Calculate the new concentration of the KOH solution.
Moles KOH = 0.025 L x 6.0 moles = 0.15 moles
1 L
New volume = 25 mL + 75 mL = 100. mL = 0.100 L
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Sound
- Space Radiation
- Waves & Sound
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Newton's laws of motion
- Gravitation