Acid and Base Balance and ImbalancePage
1
1
Slide 1
Acid and Base Balance and Imbalance
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 2
pH Review
pH = - log [H+]
H+ is really a proton
Range is from 0 - 14
If [H+] is high, the solution is acidic; pH < 7
If [H+] is low, the solution is basic or alkaline ; pH > 7
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 3
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 4
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 5
Acids are H+ donors.
Bases are H+ acceptors, or give up OH- in solution.
Acids and bases can be:
Strong – dissociate completely in solution
HCl, NaOH
Weak – dissociate only partially in solution
Lactic acid, carbonic acid
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 6
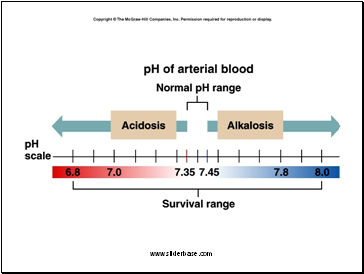
The Body and pH
Homeostasis of pH is tightly controlled
Extracellular fluid = 7.4
Blood = 7.35 – 7.45
< 6.8 or > 8.0 death occurs
Acidosis (acidemia) below 7.35
Alkalosis (alkalemia) above 7.45
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 7
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 8
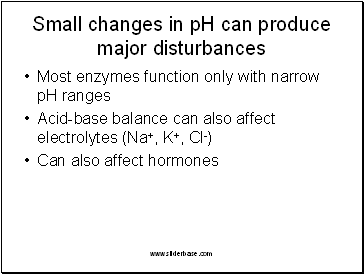
Small changes in pH can produce major disturbances
Most enzymes function only with narrow pH ranges
Acid-base balance can also affect electrolytes (Na+, K+, Cl-)
Can also affect hormones
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 9
The body produces more acids than bases
Acids take in with foods
Acids produced by metabolism of lipids and proteins
Cellular metabolism produces CO2.
CO2 + H20 ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3-
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 10
Control of Acids
Buffer systems
Take up H+ or release H+ as conditions change
Buffer pairs – weak acid and a base
Exchange a strong acid or base for a weak one
Results in a much smaller pH change
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 11
Bicarbonate buffer
Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and carbonic acid (H2CO3)
Maintain a 20:1 ratio : HCO3- : H2CO3
HCl + NaHCO3 ↔ H2CO3 + NaCl
NaOH + H2CO3 ↔ NaHCO3 + H2O
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 12
Phosphate buffer
Contents
- pH Review
- The Body and pH
- Control of Acids
- Bicarbonate buffer
- Phosphate buffer
- Protein Buffers
- Rates of correction
- Acid-Base Imbalances
- Compensation
- Acidosis
- Alkalosis
- Respiratory Acidosis
- Metabolic Acidosis
- Treatment of Metabolic Acidosis
- Metabolic Alkalosis
Last added presentations
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Thermal Energy
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Friction
- Upcoming Classes
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms