Acids and Bases. Experimental DefinitionsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Acids and Bases: Experimental Definitions
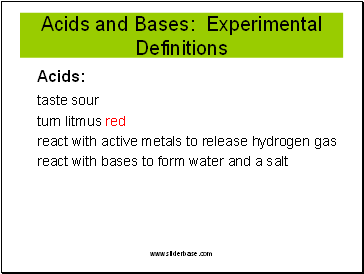
Acids:
taste sour
turn litmus red
react with active metals to release hydrogen gas
react with bases to form water and a salt
Slide 2
Acids and Bases: Experimental Definitions
Bases:
taste bitter
turn litmus blue
feel slippery
react with acids to form water and a salt
Slide 3
Acids and Bases
Slide 4
Acids, Bases, and Salts
Arrhenius Theory
Acid: a molecular substance that ionizes in aqueous solution to form hydrogen ions (H+)
Slide 5
Acids, Bases, and Salts
Arrhenius Theory
Base: a substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) in aqueous solution
Slide 6
Acids, Bases, and Salts
Neutralization: When an acid reacts with a base, the properties of each are neutralized and the products are water and a salt.
Acid + Base --> Water + Salt
Slide 7
Acids, Bases, and Salts
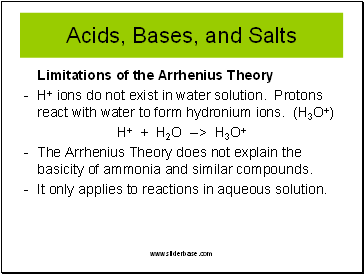
Limitations of the Arrhenius Theory
- H+ ions do not exist in water solution. Protons react with water to form hydronium ions. (H3O+)
H+ + H2O --> H3O+
The Arrhenius Theory does not explain the basicity of ammonia and similar compounds.
It only applies to reactions in aqueous solution.
Slide 8
Acids, Bases, and Salts
Brønsted-Lowry Theory
Acid: proton donor
HA + H2O --> H3O+ + A-
Base: proton acceptor
NH3 + H2O --> NH4+ + OH-
Slide 9
Nonmetal oxides are acidic
SO3 + H2O --> H2SO4
Slide 10
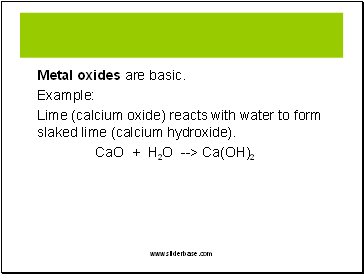
Metal oxides are basic.
Example:
Lime (calcium oxide) reacts with water to form slaked lime (calcium hydroxide).
CaO + H2O --> Ca(OH)2
Slide 11
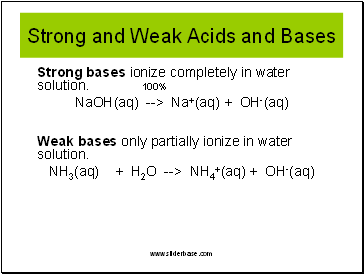
Strong and Weak Acids and Bases
Strong acids ionize completely in water solution. 100%
HCl(aq) --> H+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Weak acids only partially ionize in water solution.
HCN(aq) --> H+(aq) + CN-(aq)
Slide 12
Contents
- Acids and Bases: Experimental Definitions
- Acids and Bases
- Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Strong and Weak Acids and Bases
- Neutralization
- The pH Scale
- Acid Rain
- Antacids: A Basic Remedy
- Acids and Bases in Industry and at Home
- Acids and Bases in Health and Disease
Last added presentations
- Newton's laws of motion
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Sound
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Upcoming Classes
- Static and Kinetic Friction