EnzymesPage
1
1
Slide 1
1
Enzymes
Slide 2
2
What Are Enzymes?
Most enzymes are Proteins (tertiary and quaternary structures)
Act as Catalyst to accelerates a reaction
Not permanently changed in the process
Slide 3
3
Enzymes
Are specific for what they will catalyze
Are Reusable
End in –ase
-Sucrase
-Lactase
-Maltase
Slide 4
4
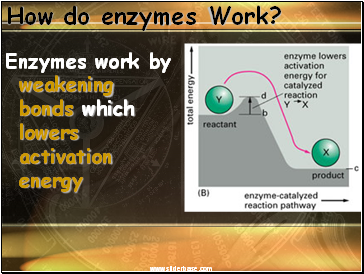
How do enzymes Work?
Enzymes work by weakening bonds which lowers activation energy
Slide 5
5
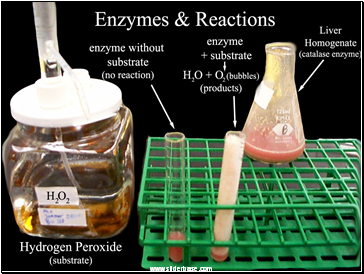
Enzymes
Slide 6
6
Slide 7
7
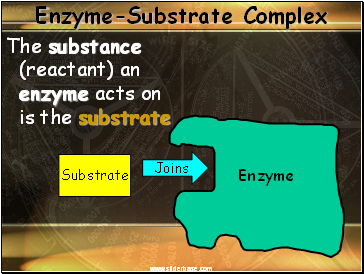
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
The substance (reactant) an enzyme acts on is the substrate
Substrate
Joins
Slide 8
8
Active Site
A restricted region of an enzyme molecule which binds to the substrate.
Substrate
Active Site
Slide 9
9
Induced Fit
A change in the shape of an enzyme’s active site
Induced by the substrate
Slide 10
10
Induced Fit
A change in the configuration of an enzyme’s active site (H+ and ionic bonds are involved).
Induced by the substrate.
Slide 11
11
What Affects Enzyme Activity?
Three factors:
1. Environmental Conditions
2. Cofactors and Coenzymes
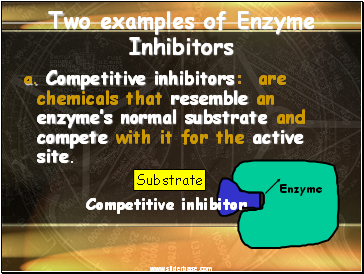
3. Enzyme Inhibitors
Slide 12
12
1. Environmental Conditions
1. Extreme Temperature are the most dangerous
- high temps may denature (unfold) the enzyme.
2. pH (most like 6 - 8 pH near neutral)
3. Ionic concentration (salt ions)
Slide 13
13
2. Cofactors and Coenzymes
Inorganic substances (zinc, iron) and vitamins (respectively) are sometimes need for proper enzymatic activity.
Example:
Iron must be present in the quaternary structure - hemoglobin in order for it to pick up oxygen.
Slide 14
1 2
Contents
- What Are Enzymes?
- How do enzymes Work?
- Enzyme-Substrate Complex
- Active Site
- Induced Fit
- Two examples of Enzyme Inhibitors
- Inhibitors
Last added presentations
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Friction
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Buoyancy
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Radiation Safety and Operations