ProteinsPage
1
1
Slide 1
PROTEINS
Slide 2
Characteristics of Proteins
Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur
Serve as structural components of animals
Serve as control molecules (enzymes)
Serve as transport and messenger molecules
Basic building block is the amino acid
Slide 3
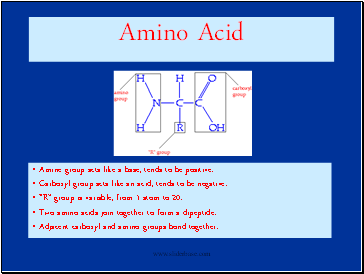
Amino Acid
Amine group acts like a base, tends to be positive.
Carboxyl group acts like an acid, tends to be negative.
“R” group is variable, from 1 atom to 20.
Two amino acids join together to form a dipeptide.
Adjacent carboxyl and amino groups bond together.
Slide 4
Some Amino Acids
Slide 5
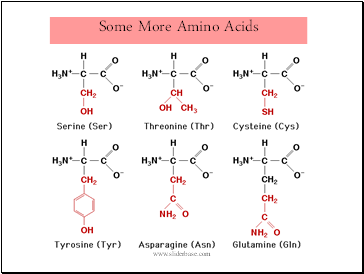
Some More Amino Acids
Slide 6
Still More Amino Acids
Slide 7
Formation of a Dipeptide
Dehydration synthesis
Slide 8
Amino Acid + Amino Acid --> Dipeptide
Amino Acid + Dipeptide --> Tripeptide
A.A. + A.A. + … + Tripeptide --> Polypeptide
Slide 9
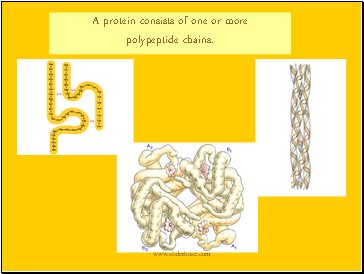
A protein consists of one or more
polypeptide chains.
Slide 10
Contents
Last added presentations
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Motion
- Radiation
- Sound
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Sound